forked from hotwax/training-assignment
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Module 2: OOPs
Rishabh Malviya edited this page Feb 7, 2023
·
1 revision
-
Encapsulation is a process of wrapping up of data under a single unit. It is the mechanism that binds together code and the data its operators.
-
In encapsulation, the data is hidden from the user and can be accessed only through the methods of their current class.
-
In Java, Java Beans is the best example of encapsulation.
class Student {
int studentId;
String studentName;
Student(int id, String name) { // parameterized constructor
studentId = id;
studentName = name;
}
// getters and setters
String getName(){ // getter for studentName
return studentName;
}
int getId(){ // getter for studentId
return studentId;
}
void setName(String name){ // setter for studentName
studentName = name;
}
void setId(int id){ // setter for studentId
studentId = id;
}
}- Inheritance is the process of borrowing the properties of one class to another class
- Inheritance is the best way to achieve code reusability.
- In Java, inheritance is achieved by using the
extendskeyword. - The class that inherits the properties of another class is called subclass or child class.
// parent class
class Science {
// method to know the course
void knowMyCourse(){
system.out.println("I am a Science Student");
}
}
// child class
class Student extends Science{
int studentId;
String studentName;
String studentCourse;
// constructor
Student(int id, String name){
studentId = id;
studentName = name;
}
}
class TestStudent{
public static void main(String[] args){
// creating object of child class
Student s1 = new Student(1, "John");
// calling method of parent class
s1.knowMyCourse();
}
}There are four types of inheritance in Java:
-
Single Inheritance
- In single inheritance, a class can inherit the properties of only one class.
- In Java, single inheritance is achieved by extending a class. This is the simplest form of inheritance.
-
Multilevel Inheritance
- In multilevel inheritance, a class can inherit the properties of another class and that class can also inherit the properties of another class.
- In Java, multilevel inheritance is achieved by extending a class which is already extended by another class.
-
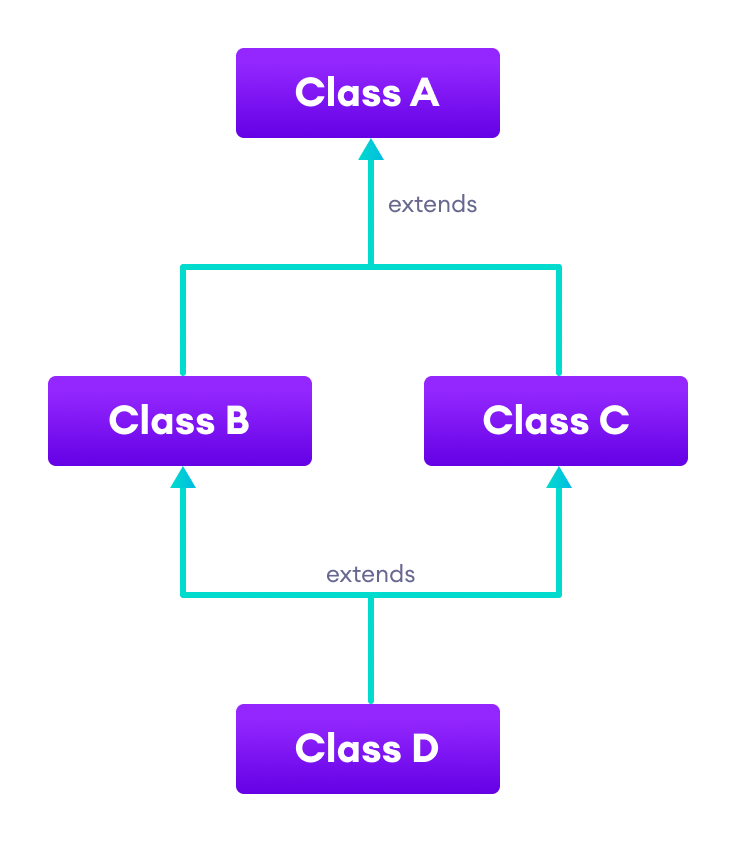
Hierarchical Inheritance
- In hierarchical inheritance, a class can inherit the properties of more than one class.
- In Java, hierarchical inheritance is achieved by extending more than one class.
-
Hybrid Inheritance
- Hybrid combination is combination of more than one type of inheritance.
- In Java, we can combine two inheritance types to achieve hybrid inheritance.
Note: In Java, multiple inheritance is not supported.
- The word polymorphism means having many forms.
- Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on many forms and perform single action in different ways.
- In Java, polymorphism is mainly divided into two types:
-
Compile-time Polymorphism
- This type of polymorphism is achieved by method overloading.
-
Runtime Polymorphism
- This type of polymorphism is achieved by method overriding.
-
Compile-time Polymorphism
class Student{
int studentId;
int subjectName;
void display(){
System.out.println("I am a student");
}
}
class Person extends Student{
String name;
void display(){
System.out.println("I am a student and Intern at HotWax Systems");
}
}- In Java, Polymorphism is mainly divided into two types:
-
Compile-time Polymorphism
- This type of polymorphism is achieved by method overloading.
- Method overloading is a feature that allows a class to have more than one method having the same name, if their argument lists are different.
- These methods are said to be overloaded and differentiated by the compiler by the number of parameters in the list and their types.
class Addition{ void add(int a, int b){ System.out.println(a+b); } void add(int a, int b, int c){ System.out.println(a+b+c); }
-
Runtime Polymorphism
- This type of polymorphism is achieved by method overriding.
- Method overriding is a feature that allows a subclass or child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its super-classes or parent classes.
class Student{ void display(){ System.out.println("I am a student"); } } class Person extends Student{ void display(){ System.out.println("I am a student and Intern at HotWax Systems"); } }
-
Compile-time Polymorphism