forked from hotwax/training-assignment
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Module 2: Exceptions
Rishabh Malviya edited this page Feb 7, 2023
·
1 revision
- Try Catch is used to handle exceptions in Java.
- Every exception is an object of a class called
Exceptionthat extends theThrowableclass. - The try block contains the code that might throw an exception. The catch block contains the code that handles the exception.
- The finally block contains the code that will be executed whether an exception is thrown or not.
class Main{
Throwable t = new Throwable();
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
throw new Exception();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception");
}finally{
System.out.println("Finally");
}
}
}
// Output: Exception
// Finally- The
try-with-resourcestatement is a try statement that declares one or more resources. - A resource is an object that must be closed after the program is finished with it.
- The
try-with-resourcestatement ensures that each resource is closed at the end of the statement.
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
try(FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("resource.txt")){ // file is a resource
while(file.readLine() != null){
System.out.println(file.readLine());
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.print(e.getMessage());
}
}
}- The
finallyblock is used to execute important code such as closing connection, streams etc. - The
finallyblock is always executed whether an exception is handled or not.
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
System.out.println("I am Try"); // It will try to execute
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("I am Catch"); // It will execute only when exception is thrown
}finally{
System.out.println("I am Finally"); // It will always execute
}
}
}
// Output: Try
// Finally- The
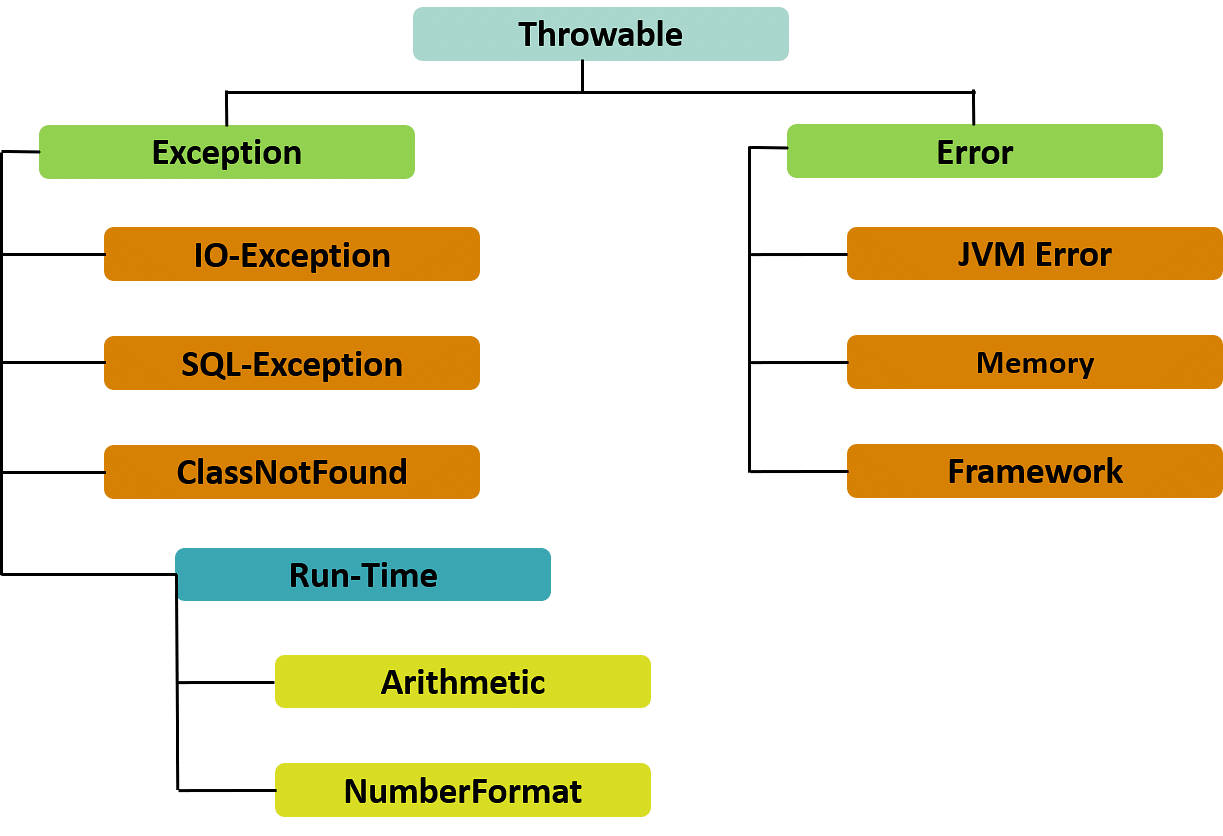
Throwableclass is the root of the Java exception hierarchy. - The
Exceptionclass and its subclasses are a form ofThrowablethat indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch. - The
Errorclass and its subclasses are a form ofThrowablethat indicates serious problems that a reasonable application should not try to catch. - The
RuntimeExceptionand its subclasses are a form ofExceptionthat indicates conditions that a reasonable application might want to catch. - The
Exceptionclass and any subclasses that are not also subclasses ofRuntimeExceptionare checked exceptions.