-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Module 1
Welcome to the training-assignment wiki!
Git is a modern and widely used distributed version control system in the world. It is developed to manage projects with high speed and efficiency. The version control system allows us to monitor and work together with our team members at the same workspace. GitHub is a Git repository hosting service. GitHub also facilitates many of its features, such as access control and collaboration. It provides a Web-based graphical interface.
It includes operating system settings, hardware configuration, software configuration, test terminals, and other support to perform the operations.
Git supports a command called git config that lets you get and set configuration variables that control all facets of how Git looks and operates. It is used to set Git configuration values on a global or local project level.
Setting user.name and user.email are the necessary configuration options as your name and email will show up in your commit messages.Setting username-
git config --global user.name "Name"
git config --global user.email "email"
git config -list
The git config command can accept arguments to specify the configuration level. The following configuration levels are available in the Git config.
-
local- It is the default level in Git. Git config will write to a local level if no configuration option is given.
-
global- The global level configuration is a user-specific configuration. User-specific means, it is applied to an individual operating system user.
-
system- The system-level configuration is applied across an entire system. The entire system means all users on an operating system and all repositories.
Repositories in contain a collection of files of various different versions of a Project. These files are imported from the repository into the local server of the user for further updations and modifications in the content of the file. A VCS or the is used to create these versions and store them in a specific place termed a repository. The process of copying the content from an existing Git Repository with the help of various Git Tools is termed cloning.
It is used to record the changes in the repository. It is the next command after the git add. Every commit contains the index data and the commit message. When we add a file in Git, it will take place in the staging area. A commit command is used to fetch updates from the staging area to the repository.
git commit
It will prompt a default editor and ask for a commit message.
git commit -a
The commit command also provides a -a option to specify some commits. It is used to commit the snapshots of all changes. This option only consider already added files in Git. It will not commit the newly created files.
git commit -m "commit message"
The -m option of the commit command lets you write the commit message on the command line.
- Tracked: Tracked files are such files that are previously staged or committed.
- Untracked: Untracked files are such files that are not previously staged or committed.
- Ignored: Ignored files are such files that are explicitly ignored by git. We have to tell git to ignore such files.
- Staged: The file has been added to its version control but changes have not been committed. Git status is used to understand what stage the files in a repository are at.
The term "ignore" is used to specify intentionally untracked files that Git should ignore. It doesn't affect the Files that are already tracked by Git. How to Ignore Files Manually- Create a file named .gitignore if you do not have it already in your directory. Now, add the files and directories to the .gitignore file that you want to ignore. To add the files and directory to the .git ignore the file, open the file and type the file name, directory name, and pattern to ignore files and directories. Now, to share it on Git, we have to commit it.
Git diff is a command-line utility. It's a multiuse Git command. When it is executed, it runs a diff function on Git data sources. These data sources can be files, branches, commits, and more. It is used to show changes between commits, commit, working tree, etc.
git diff <commit1> <commit2>
The git diff command lets track the changes between two commits.
git diff --staged
To check the staged changes, run the git diff command along with the --staged option.
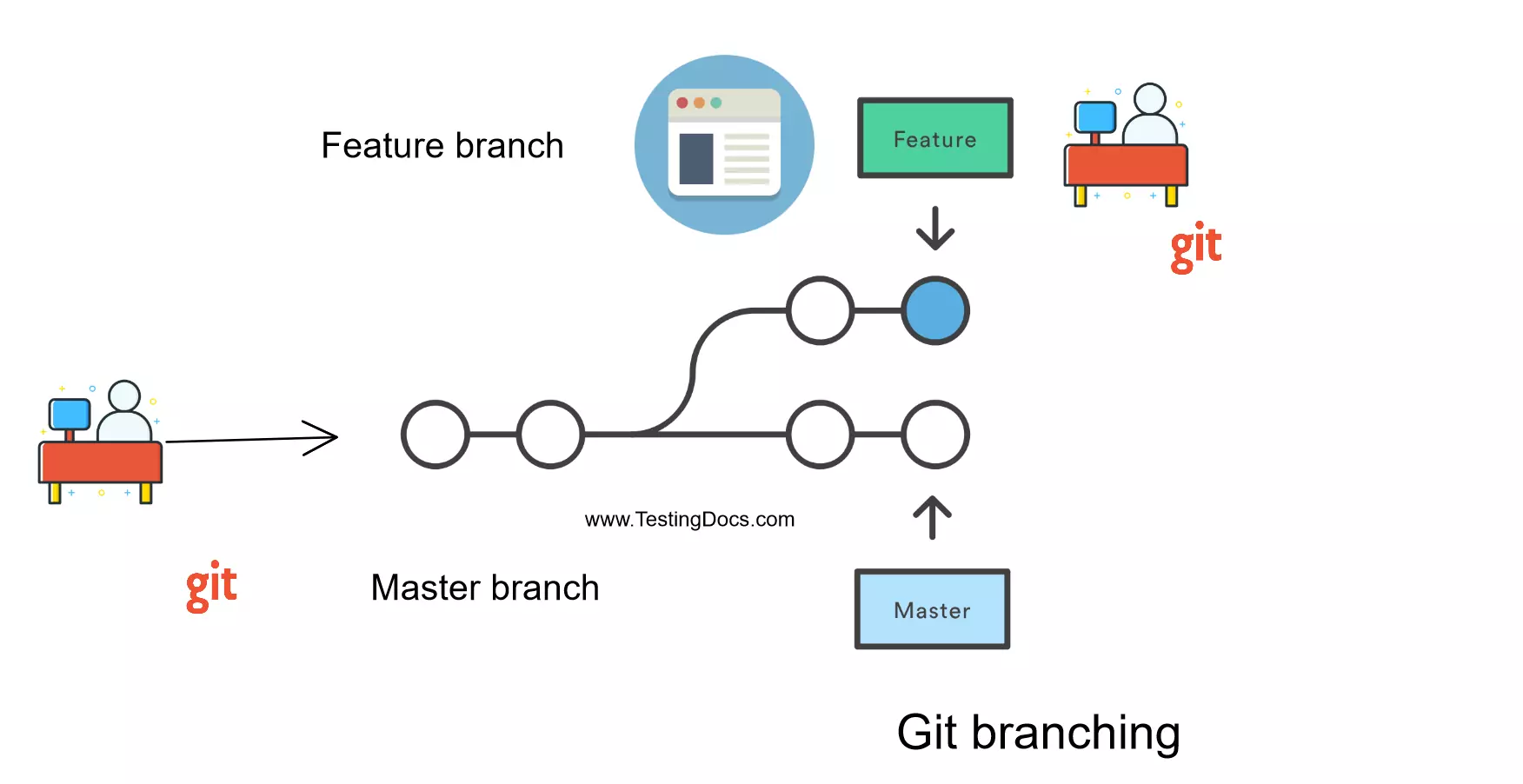
A branch is a version of the repository that diverges from the main working project. It is a feature available in most modern version control systems. A Git project can have more than one branch. These branches are a pointer to a snapshot of your changes.A branch is a version of the repository that diverges from the main working project. It is a feature available in most modern version control systems. A Git project can have more than one branch. These branches are a pointer to a snapshot of your changes. When you want to add a new feature or fix a bug, you spawn a new branch to summarize your changes. So, it is complex to merge the unstable code with the main code base and it also facilitates you to clean up your future history before merging with the main branch.
The master branch is a default branch in Git. It is instantiated when the first commit is made to the project. When you make the first commit, you're given a master branch to the starting commit point. The git branch command allows you to create, list, rename and delete branches.
git branch <branch name>
git branch --list
git branch -d <branch name>
git push origin -delete <branch name>
git checkout<branch name>
git branch -m <old branch name><new branch name>
git merge <branch name>
Git log is a utility tool to review and read a history of everything that happens to a repository. Multiple options can be used with a git log to make history more specific. Generally, the git log is a record of commits. A git log contains the following data:
A commit hash is a 40-character checksum data generated by SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) algorithm. It is a unique number.
- Commit Author metadata: The information of authors such as author name and email.
- Commit Date metadata: It's a date timestamp for the time of the commit.
- Commit title/message: It is the overview of the commit given in the commit message.
git log
The term reset stands for undoing changes. The git reset command is used to reset the changes. The git reset command has three core forms of invocation. These forms are as follows.
The soft option does not touch the index file or working tree at all, but it resets the Head as all options do. When the soft mode runs, the refs pointers are updated, and the resets stop there. It will act as a git amend command.
git reset --soft commit-id
A mixed option is a default option of the git reset command. If we would not pass any argument, then the git reset command is considered as --mixed as the default option. A mixed option updates the ref pointers. The staging area also reset to the state of a specified commit. The undone changes are transferred to the working directory.
git reset --mixed
It will first move the Head and update the index with the contents of the commits. It is the most direct, unsafe, and frequently used option. The --hard option changes the Commit History, and ref pointers are updated to the specified commit. Then, the Staging Index and Working Directory need to reset to match that of the specified commit. Any previously pending commits to the Staging Index and the Working Directory get reset to match Commit Tree. It means any awaiting work will be lost.
git reset --hard
In Git, the term revert is used to revert some changes. The git revert command is used to apply the revert operation. It is an undo-type command. However, it is not a traditional undo alternative. It does not delete any data in this process; instead, it will create a new change with the opposite effect and thereby undo the specified commit. Generally, git revert is a commit. If you want to remove something from history then git revert is the wrong choice.
git revert
< commit>: The commit option is used to revert a commit. To revert a commit, we need the commit reference id. The git log command can access it.
git revert <commit-id>
It is used to edit the commit message before reverting the commit. It is a default option in the git revert command.
Cherry-picking in Git stands for applying some commit from one branch into another branch. In case you made a mistake and committed a change into the wrong branch, but do not want to merge the whole branch. You can revert the commit and apply it on another branch.
Suppose you are working with a team of developers on a medium to large-sized project. Some changes were proposed by another team member and you want to apply some of them to your main project, not all. Managing the changes between several Git branches can become a complex task, and you don't want to merge a whole branch into another branch. You only need to pick one or two specific commits. To pick some changes to your main project branch from other branches is called cherry-picking.
git cherry-pick <commit id>
The "git merge" command- The git merge command is used to merge the branches. It can be used in various contexts. Some are as follows:
-
Scenario 1: To merge the specified commit to the currently active branch -
Scenario 2: To merge commits into the master branch.
Git Merge Conflict- When two branches are trying to merge, and both are edited at the same time and in the same file, Git won't be able to identify which version to take for changes. Such a situation is called a merge conflict. If such a situation occurs, it stops just before the merge commit so that you can resolve the conflicts manually.
Resolve Conflict: git mergetool- To resolve the conflict, it is necessary to know whether the conflict occurs and why it occurs. The Git merge tool command is used to resolve the conflict.
git rebase --continue
To resolve the conflict, enter the insert mode by merely pressing the I key and making changes as you want. Press the Esc key, to come out from insert mode. Type the: w! at the bottom of the editor to save and exit the changes. To accept the changes, use the rebase command.
Sometimes you want to switch branches, but you are working on an incomplete part of your current project. You don't want to make a commit to half-done work. Git stashing allows you to do so. The git stash command enables you to switch branches without committing to the current branch. Generally, the stash's meaning is "store something safely in a hidden place." The sense in Git is also the same for stash; Git temporarily saves your data safely without committing.
git stash
In Git, the term remote is concerned with the remote repository. It is a shared repository that all team members use to exchange their changes. A remote repository is stored on a code hosting services like an internal server, GitHub, Subversion, and more.
The developers can perform many operations with the remote server. These operations can be a clone, fetch, push, pull, and more.
git remote
The git remote command allows accessing the connection between remote and local.
git remote -v
To show the URLs that Git has stored as a short name
git remote add <short name><remote URL>
When we fetch a repository implicitly, git adds a remote for the repository. Also, we can explicitly add a remote for a repository. We can add a remote as a shot nickname or short name.
git remote set-url <remote name><newURL>
we can change the URL Of a remote repository. The git remote set command is used to change the URL of the repository.
The push term refers to uploading local repository content to a remote repository. Pushing is an act of transferring commits from your local repository to a remote repository. Pushing is capable of overwriting changes.
git push <option> [<Remote URL><branch name>]
git push origin master
Generally, the term origin stands for the remote repository, and master is considered the main branch. So, the entire statement "git push origin master" pushed the local content on the master branch of the remote location.
The git pull command is used to fetch and download content from a remote repository and immediately update the local repository to match that content. Merging remote upstream changes into your local repository is a common task in Git-based collaboration work flows.
git pull <option> [<repository URL>]
The pull command is used to access the changes (commits)from a remote repository to the local repository. It updates the local branches with remote-tracking branches. Remote tracking branches are branches that have been set up to push and pull from the remote repository. Generally, it is a collection of the fetch and merges commands. First, it fetches the changes from the remote and combined them with the local repository.
GitHub is a repository hosting service tool that features collaboration and access control. It is a platform for programmers to fix bugs together and host open-source projects. GitHub is designed for the developers and to help them track their changes into a project through the repository. GitHub is not open source. It allows users to have unlimited free repository.
GitLab is a repository hosting manager tool that is developed by GitLab Inc and is used for the software development process. It provides a variety of management by which we can streamline our collaborative workflow for completing the software development lifecycle. It also allows us to import the repository from Google Code, Bitbucket, etc. It allows users to make public repository. GitLab provides the feature of navigation into the repository.
A merge request (also known as pull request) is the request to review newly written code by several colleagues before the code becomes a definitive part of the software. These reviews make sure the code is checked whether it is correct, has been written clearly and meets the agreed standards.
git merge <name of the branch to be merged>
pull requests are a mechanism for a developer to notify team members that they have completed a feature. Once their feature branch is ready, the developer files a pull request via their Bitbucket account. This lets everybody involved know that they need to review the code and merge it into the main branch.

Forking is a git clone operation executed on a server copy of a projects repo. A Forking Workflow is often used in conjunction with a Git hosting service like Bitbucket. A high-level example of a Forking Workflow is: You want to contribute to an open source library hosted at bitbucket.org/userA/open-project.