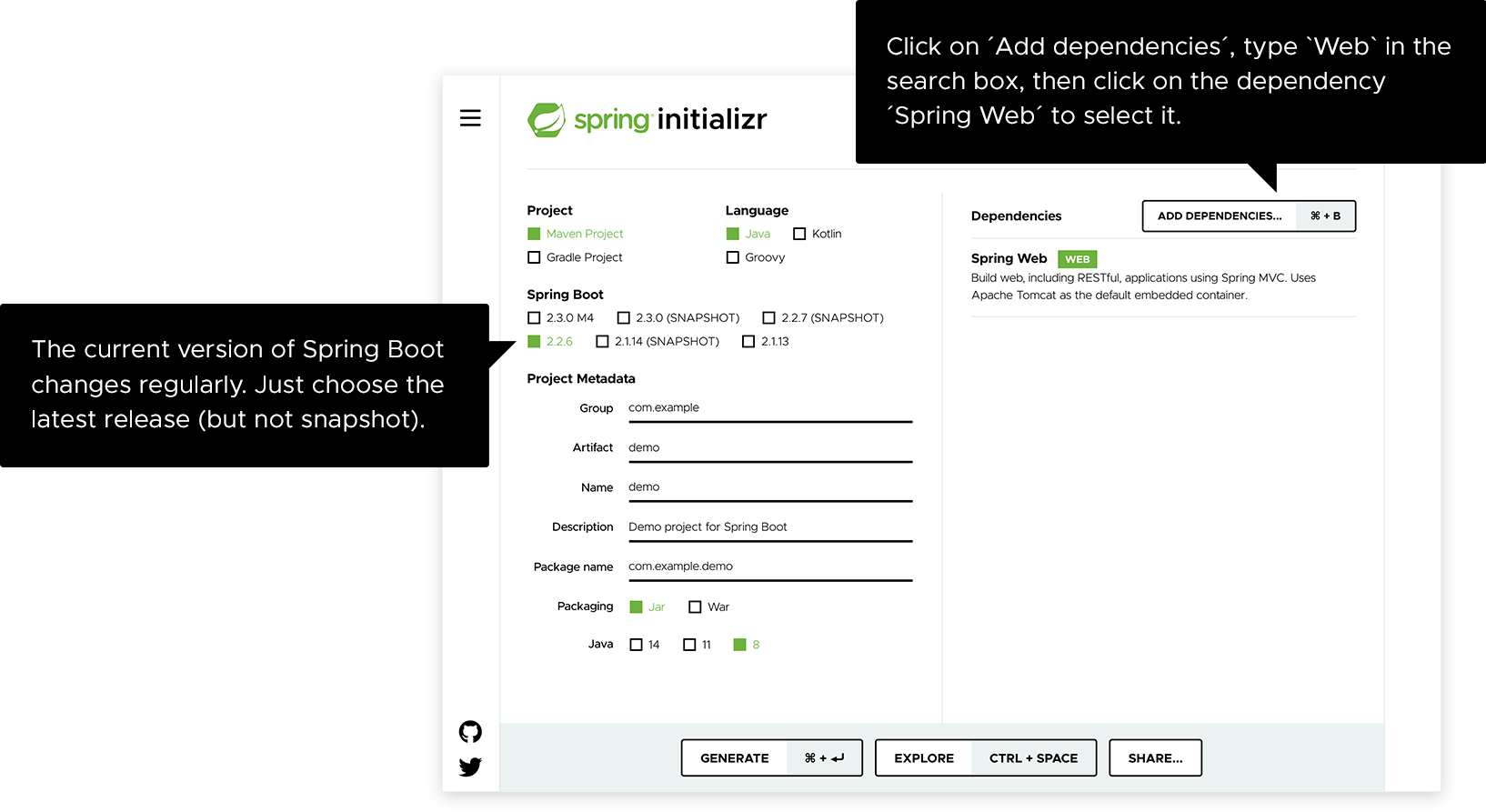
Use start.spring.io to create a “web” project. In the “Dependencies” dialog search for and add the “web” dependency as shown in the screenshot. Hit the “Generate” button, download the zip, and unpack it into a folder on your computer.
Projects created by start.spring.io contain Spring Boot, a framework that makes Spring ready to work inside your app, but without much code or configuration required. Spring Boot is the quickest and most popular way to start Spring projects.
Open up the project in your IDE and locate the DemoApplication.java file in the src/main/java/com/example/demo folder. Now change the contents of the file by adding the extra method and annotations shown in the code below. You can copy and paste the code or just type it.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication @RestController public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); }
@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "World") String name) { return String.format("Hello %s!", name); } }