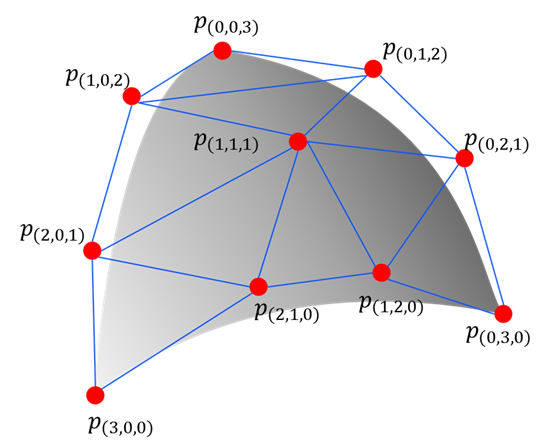
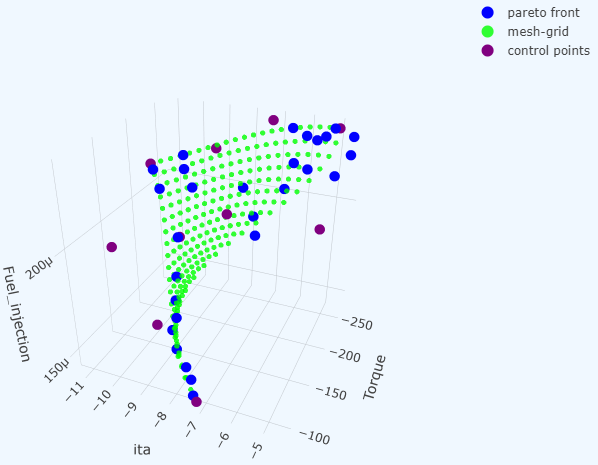
A PyTorch implementation of Bezier simplex fitting.
The Bezier simplex is a high-dimensional generalization of the Bezier curve. It enables us to model a complex-shaped point cloud as a parametric hyper-surface in high-dimensional spaces. This package provides an algorithm to fit a Bezier simplex to given data points. To process terabyte-scale data, this package supports distributed training, realtime progress reporting, and checkpointing on top of PyTorch Lightning and MLflow.
See the following papers for technical details.
- Kobayashi, K., Hamada, N., Sannai, A., Tanaka, A., Bannai, K., & Sugiyama, M. (2019). Bézier Simplex Fitting: Describing Pareto Fronts of´ Simplicial Problems with Small Samples in Multi-Objective Optimization. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 33(01), 2304-2313. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33012304
- Tanaka, A., Sannai, A., Kobayashi, K., & Hamada, N. (2020). Asymptotic Risk of Bézier Simplex Fitting. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34(03), 2416-2424. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i03.5622
Python >=3.10, <3.14.
Download the latest Miniconda and install it. Then, install MLflow on your conda environment:
conda install -c conda-forge mlflowPrepare data:
cat <<EOS > params.csv
1.00, 0.00
0.75, 0.25
0.50, 0.50
0.25, 0.75
0.00, 1.00
EOS
cat <<EOS > values.csv
0.00, 1.00
3.00, 2.00
4.00, 5.00
7.00, 6.00
8.00, 9.00
EOSRun the following command:
mlflow run https://github.com/rafcc/pytorch-bsf \
-P params=params.csv \
-P values=values.csv \
-P meshgrid=params.csv \
-P degree=3which automatically sets up the environment and runs an experiment:
- Download the latest pytorch-bsf into a temporary directory.
- Create a new conda environment and install dependencies in it.
- Run an experiment on the temporary directory and environment.
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| params | path | required | The parameter data file, which contains input observations for training a Bezier simplex. The file must be of CSV (.csv) or TSV (.tsv). Each line in the file represents an input observation, corresponding to an output observation in the same line in the value data file. |
| values | path | required | The value data file, which contains output observations for training a Bezier simplex. The file must be of CSV (.csv) or TSV (.tsv). Each line in the file represents an output observation, corresponding to an intput observation in the same line in the parameter data file. |
| init | path | None |
Load initial control points from a file. The file must be of pickled PyTorch (.pt), CSV (.csv), TSV (.tsv), JSON (.json), or YAML (.yml or .yaml). Either this option or --degree must be specified, but not both. |
| degree | int |
None |
Generate initial control points at random with specified degree. Either this option or --init must be specified, but not both. |
| fix | list[list[int]] | None |
Indices of control points to exclude from training. By default, all control points are trained. |
| header | int |
0 |
The number of header lines in params/values files. |
| normalize |
"max", "std", "quantile"
|
None |
The data normalization: "max" scales each feature as the minimum is 0 and the maximum is 1, suitable for uniformly distributed data; "std" does as the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1, suitable for nonuniformly distributed data; "quantile" does as 5-percentile is 0 and 95-percentile is 1, suitable for data containing outliers; None does not perform any scaling, suitable for pre-normalized data. |
| split_ratio | float |
0.5 |
The ratio of training data against validation data. |
| batch_size | int |
0 |
The size of minibatch. The default uses all records in a single batch. |
| max_epochs | int |
1000 |
The number of epochs to stop training. |
| accelerator |
"auto", "cpu", "gpu", etc. |
"auto" |
Accelerator to use. See PyTorch Lightning documentation. |
| strategy |
"auto", "dp", "ddp", etc. |
"auto" |
Distributed strategy. See PyTorch Lightning documentation. |
| devices | int |
"auto" |
The number of accelerators to use. By default, use all available devices. See PyTorch Lightning documentation. |
| num_nodes | int |
1 |
The number of compute nodes to use. See PyTorch Lightning documentation. |
| precision |
"64", "32", "16", "bf16"
|
"32" |
The precision of floating point numbers. |
| loglevel | int |
2 |
What objects to be logged. 0: nothing; 1: metrics; 2: metrics and models. |
| enable_checkpointing | bool | False |
With this flag, model files will be stored every epoch during training. |
| log_every_n_steps | int |
1 |
The interval of training steps when training loss is logged. |
pip install pytorch-bsfThis package provides a command line interface to train a Bezier simplex with a dataset file.
Execute the torch_bsf module:
python -m torch_bsf \
--params=params.csv \
--values=values.csv \
--meshgrid=params.csv \
--degree=3Train a model by fit(), and call the model to predict.
import torch
import torch_bsf
# Prepare training data
ts = torch.tensor( # parameters on a simplex
[
[8 / 8, 0 / 8],
[7 / 8, 1 / 8],
[6 / 8, 2 / 8],
[5 / 8, 3 / 8],
[4 / 8, 4 / 8],
[3 / 8, 5 / 8],
[2 / 8, 6 / 8],
[1 / 8, 7 / 8],
[0 / 8, 8 / 8],
]
)
xs = 1 - ts * ts # values corresponding to the parameters
# Train a model
bs = torch_bsf.fit(params=ts, values=xs, degree=3)
# Predict by the trained model
t = [
[0.2, 0.8],
[0.7, 0.3],
]
x = bs(t)
print(f"{t} -> {x}")See documents for more details. https://rafcc.github.io/pytorch-bsf/
RIKEN AIP-FUJITSU Collaboration Center (RAFCC)
MIT