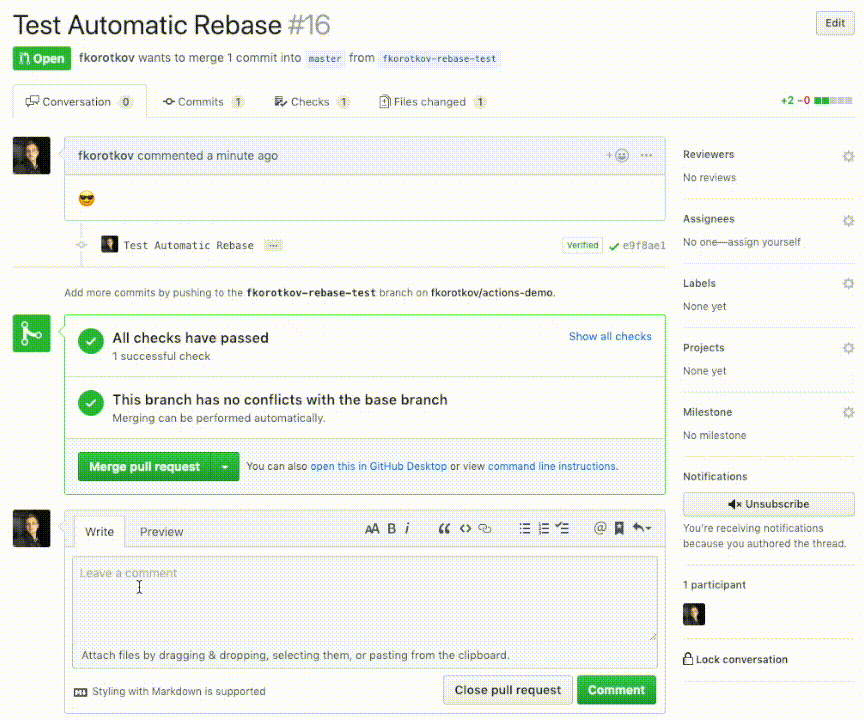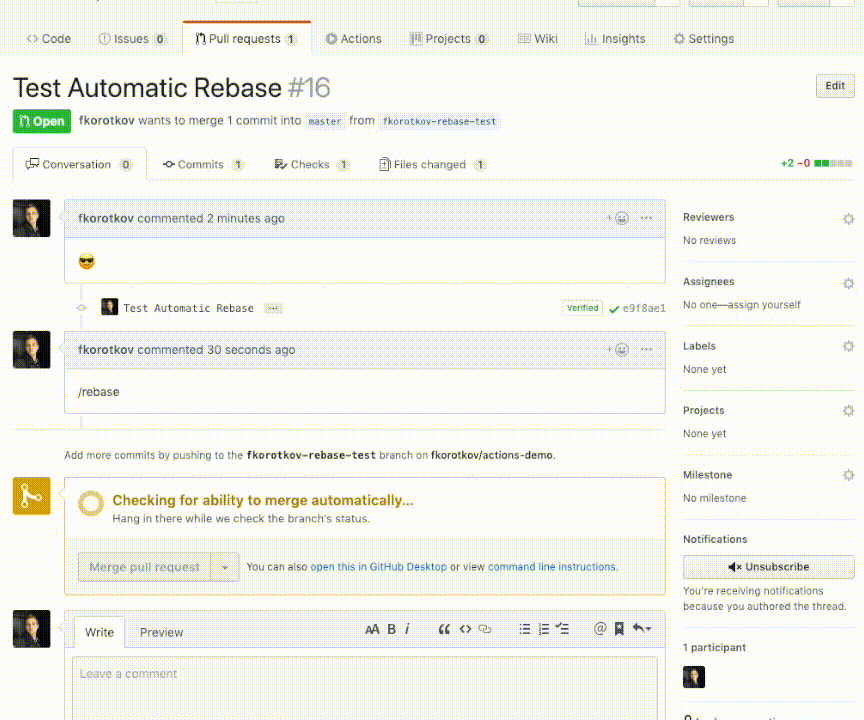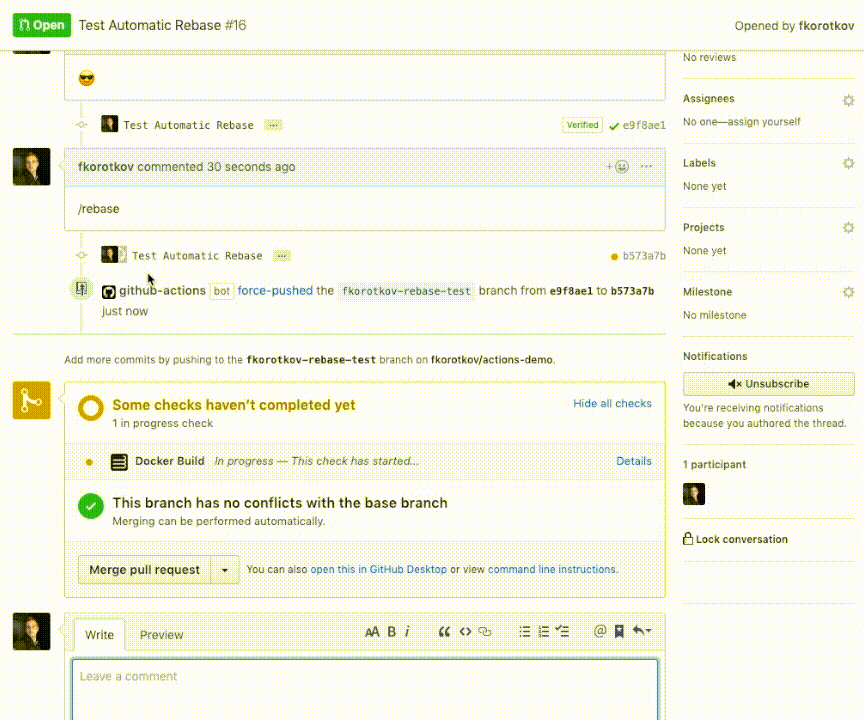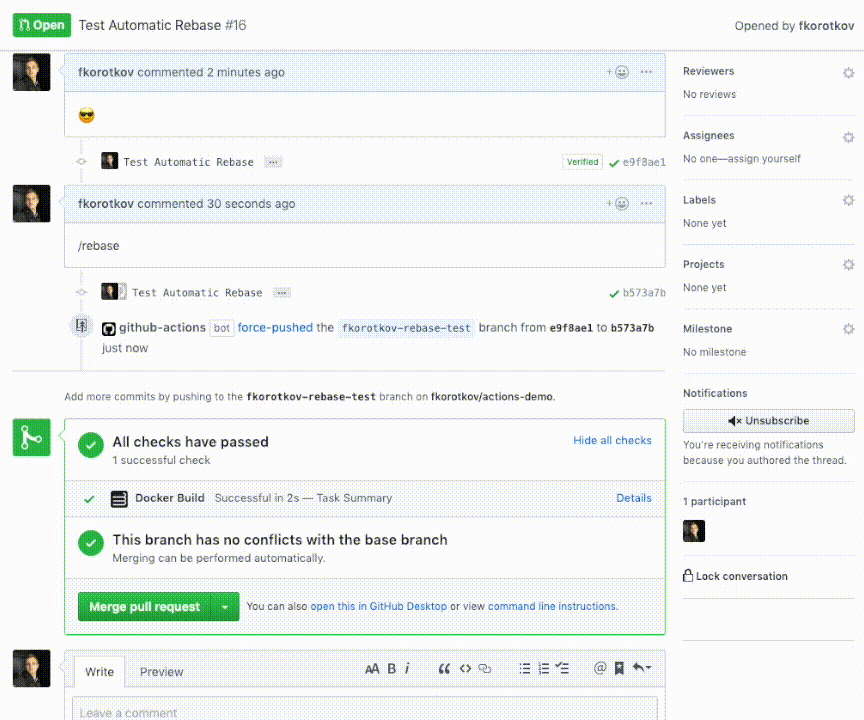
After installation simply comment /rebase to trigger the action:
To configure the action simply add the following lines to your .github/workflows/rebase.yml workflow file:
name: Automatic Rebase
on:
issue_comment:
types: [created]
jobs:
rebase:
name: Rebase
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: >-
github.event.issue.pull_request != '' &&
(
contains(github.event.comment.body, '/rebase') ||
contains(github.event.comment.body, '/autosquash')
)
steps:
- name: Checkout the latest code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
fetch-depth: 0 # otherwise, you will fail to push refs to dest repo
- name: Automatic Rebase
uses: cirrus-actions/rebase@1.8
with:
autosquash: ${{ contains(github.event.comment.body, '/autosquash') || contains(github.event.comment.body, '/rebase-autosquash') }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
REBASE_USERNAME: 'your-github-username'
REBASE_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.REBASE_TOKEN }}
REBASE_KEY: ${{ secrets.REBASE_KEY }}This action requires three secrets to be configured:
A Personal Access Token with repo scope for API access.
Setup:
- Go to GitHub Settings → Developer settings → Personal access tokens → Tokens (classic)
- Click "Generate new token (classic)"
- Select the
reposcope - Generate and copy the token
- Add it to your repository secrets as
REBASE_TOKEN
An SSH private key (deploy key) for git operations on fork repositories. This bypasses organization PAT restrictions.
Setup:
-
Generate an SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "rebase-action" -f rebase_key -N ""
-
Add the public key (
rebase_key.pub) as a deploy key to the fork repository:- Go to fork repository Settings → Deploy keys → Add deploy key
- Title: "Rebase Action"
- Key: paste contents of
rebase_key.pub - ✅ Allow write access (required for pushing)
-
Add the private key (
rebase_key) to repository secrets asREBASE_KEY:- Go to base repository Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions
- New repository secret
- Name:
REBASE_KEY - Value: paste entire contents of
rebase_keyfile (including-----BEGINand-----ENDlines)
Your GitHub username (the owner of the fork). Set this in the workflow env section.
This action uses SSH keys for git operations (fetch/push) instead of Personal Access Tokens because:
- Many organizations restrict PAT usage in GitHub Actions for security
- SSH deploy keys work reliably across organization boundaries
- PATs work fine for API calls but may fail for git operations from Actions runners
Example complete workflow:
name: Automatic Rebase
on:
issue_comment:
types: [created]
jobs:
rebase:
name: Rebase
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: >-
github.event.issue.pull_request != '' &&
(
contains(github.event.comment.body, '/rebase') ||
contains(github.event.comment.body, '/autosquash')
)
steps:
- name: Checkout the latest code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Automatic Rebase
uses: cirrus-actions/rebase@1.8
with:
autosquash: ${{ contains(github.event.comment.body, '/autosquash') }}
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
REBASE_USERNAME: 'your-github-username'
REBASE_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.REBASE_TOKEN }}
REBASE_KEY: ${{ secrets.REBASE_KEY }}It's possible to use author_association field of a comment to restrict who can call the action and skip the rebase for others. Simply add the following expression to the if statement in your workflow file: github.event.comment.author_association == 'MEMBER'. See documentation for a list of all available values of author_association.
GitHub can also optionally dismiss an existing review automatically after rebase, so you'll need to re-approve again which will trigger the test workflow. Set it up in your repository Settings > Branches > Branch protection rules > Require pull request reviews before merging > Dismiss stale pull request approvals when new commits are pushed.