This project includes a C++ implementation of the Banker's Algorithm for deadlock avoidance. This implementation is meant to determine whether a system is in a deadlocked state through the input of a text file showing the current state.
- Linux environment (Testing was done on Ubuntu in VirtualBox)
- GCC Compiler
- Terminal
- Clone the repository OR download the files by navigating to the folder titled "C++"
- Open the folder in your Linux terminal
- Make sure to have GCC up to date (gcc --version)
- Compile using a couple commands:
- g++ bankersalgorithm.cpp -o bankersalgorithm
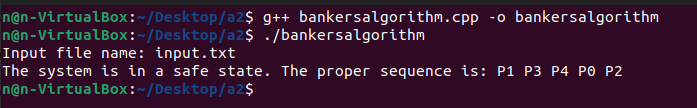
- ./bankersalgorithm
- Input the name of the input file you would like to use
- ex:
input.txtorinput-2.txt - Do not include quotation marks
- Success!
The banker's algorithm is a deadlock avoidance algorithm. It is based on the real-world banking system, taking inspiration from how they decide whether to grant a loan or not. The idea is that there are N account holders at a bank, and the sum of all of their money is S. Every time a loan is granted, they subtract the loan amount from the total money the bank has. If the resulting value is greater than S, that means they have enough money to grant the loan even if all of the account holders draw out their money.
In regards to operating systems, the banker's algorithm must decide when they can or can not lend out a resource to a process or processes. Since there are limited resources in the system, the system is in an unsafe state if the needed resources are greater than the available resources. In terms of a real-world bank, the money being requested exceeds the amount of money the bank has in its possession.
In this particular implementation, the program finds the correct sequence in which the processes have to run in order to avoid deadlock based on the current state of the system. If the current state is unsafe or has deadlock, it will not be able to return a sequence since a safe sequence does not exist. The program finds the correct sequence by calculating the need of each of the processes as a matrix. It will then use this matrix along with the matrix of available resources to calculate whether the need for the processes exceeds the current available resources. The program follows a process of elimination from here, eliminating processes that are able to finish their work until all processes have finished their work. It will then check if the sequence it eliminated the processes in is correct, and if so, that is the sequence that the processes need to run in order to avoid deadlock.
Note: The provided input.txt was used as the input file.
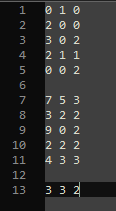
You can customize the program by creating your own input file. The input file, however, must follow a certain format. The format is as follows:
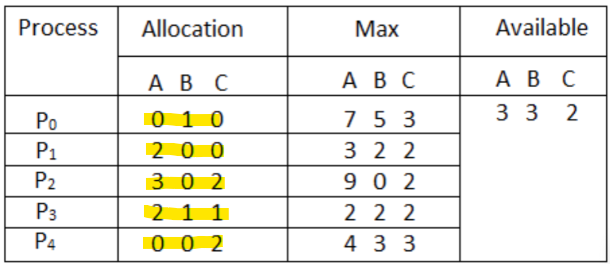
First block, input allocation matrix:
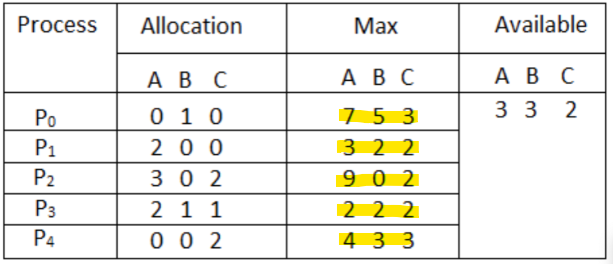
Second block, input max matrix:
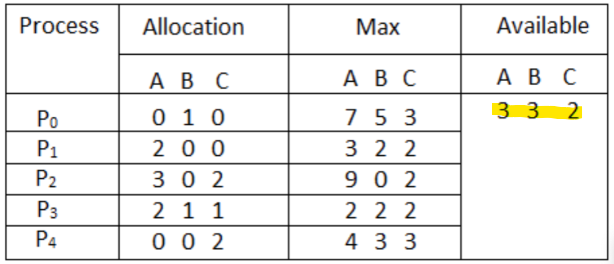
Third block, input available matrix:
Each number should be delimited by a space, and each process should be delimited by a line. Each block should have an empty line between them. Your input file should end up looking like this:
- nmarhari
- This implementation was created by Nassim Marhari. It is based on the Banker's Algorithm.