FDRecovery is a quick and easy to use data recovery tool which allows the user to select which files they wish to recover. It allows users who accedentally delete files to recover the desired file in a simple and time sensitive manner. On linux systems, ext2/3/4 are supported, and on windows systems exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS are the supported file systems.
First, make sure you have python3 installed:
You can do this on windows from the microsoft store or here: https://www.python.org/downloads/
Most linux systems will already have python3 installed, but on debian based systems you can use this command:
sudo apt install python3
On arch linux systems use:
sudo pacman -Syu python3
You also must have the tkinter python module. If you already have python3 installed, the following command should work on both windows and linux systems:
pip install tk
Next clone this repository using git:
git clone https://github.com/jdafoe12/FDRecovery.git
To run FDRecovery you must have administrator privlidges. In windows run command prompt as administrator and in linux systems use sudo with the following command:
python3 -m path.to.FDRecovery.src.filesystem
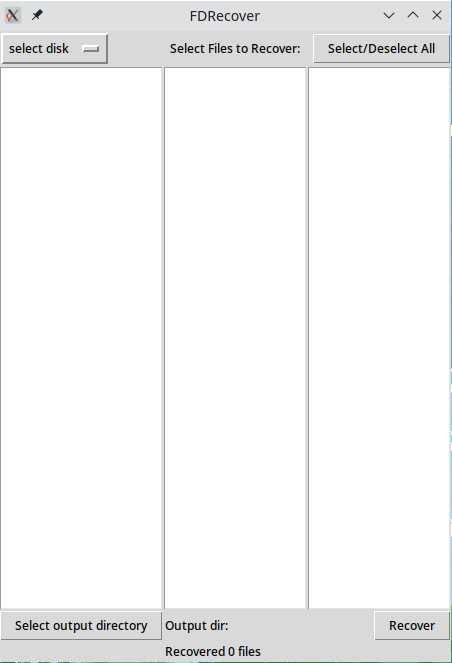
where path.to.FDRecovery is your path to the repository and filesystem is EXT, FAT, or NTFS, depending on the filesystem of the storage device you wish to recover data from. This will open the tool as a window which looks like this:
From here you can select the storage device you wish to recover data from the dropdown menu by clicking the select disk button. Once it is finished processing, deleted files will be displayed in the three middle boxes:
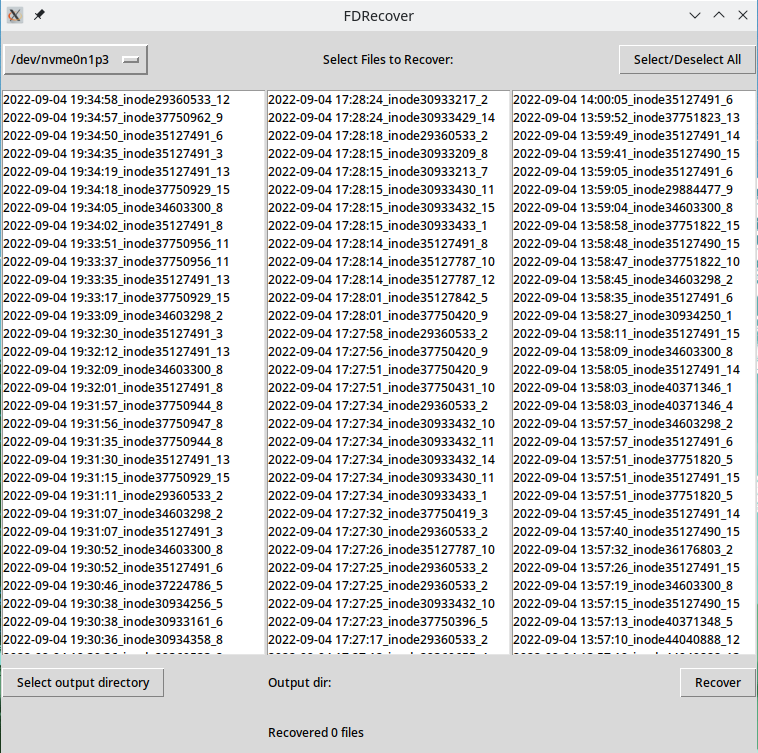
You can now select the files you wish to recover by clicking on them in the boxes. In EXT2/3/4, the files are identifiable based on deletion time as seen above, while in exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS, the files are identifiable based on the file name. In order to recover the selected files, you must select an output directory by clicking the associated button. Then you can simply click the recover button, and the recovered files will be contained in the selected output directory.
