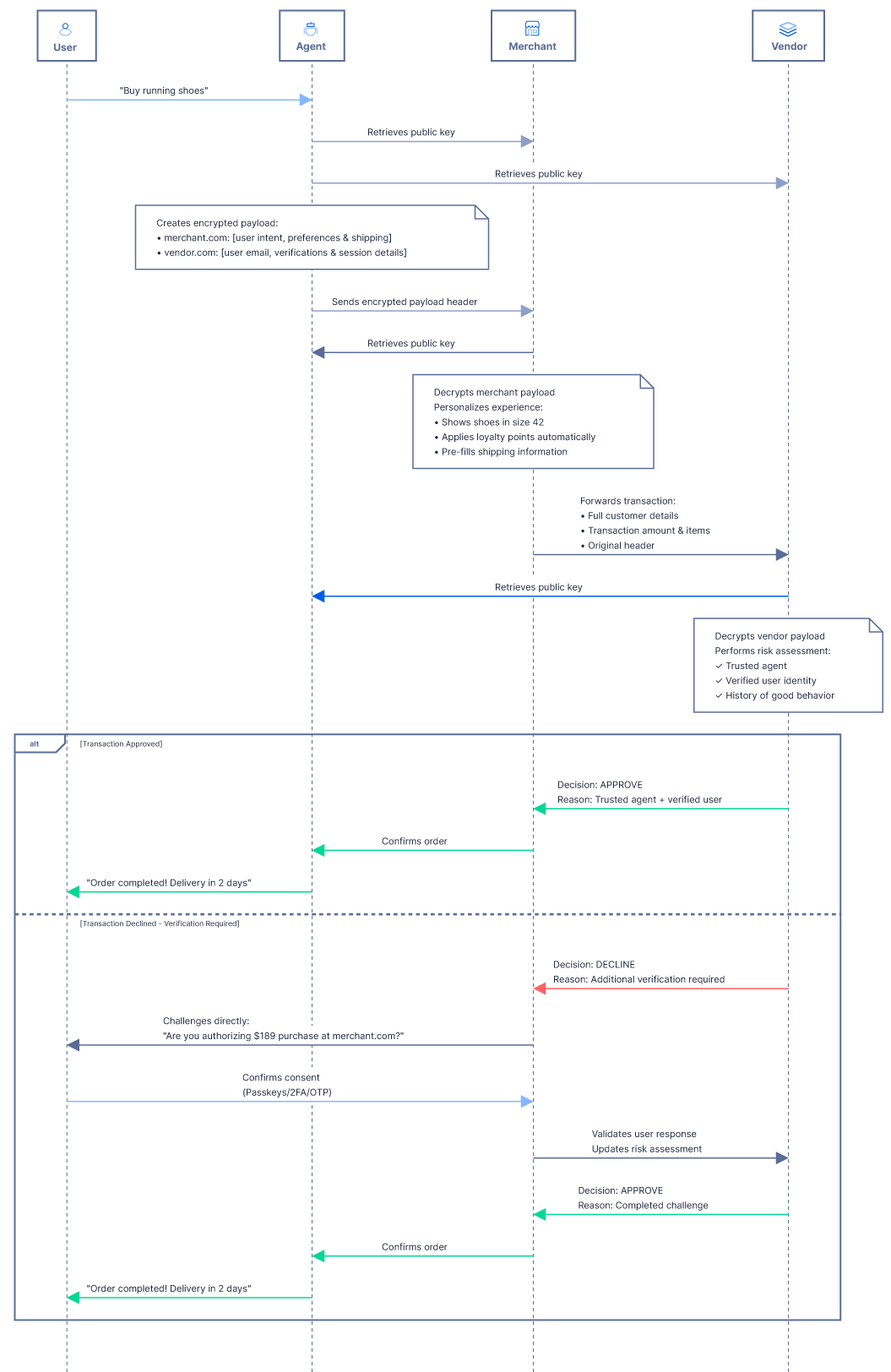
A secure authentication and data encryption protocol that allows AI agents, merchants and merchant vendors:
- ✅ Authenticate each other: verify the agent's identity and its relationship to the customer behind it
- ✅ Maintain rich customer data: reduce data losses and increase agents approval rate
- ✅ Improve user experience: create personalized, secure and frictionless checkout experience
- ✅ Prevent fraud: differentiates between legitimate agentic activity and fraud attempts
🎉 Read the announcement on Forter Blog
- JavaScript - Node.js >=18.0.0
- TypeScript - Node.js >=18.0.0
- Python - Python >=3.8
- More coming soon!
Trusted Agentic Commerce Protocol relies on:
- JWS+JWE Security: JWT signatures (JWS) wrapped in JSON Web Encryption (JWE) for both authentication and confidentiality
- RSA Key Support: Compatible with RSA keys (minimum 2048-bit, 3072-bit recommended) for signing and encryption
- JSON Web Key Sets (JWKS): Standard key distribution at
.well-known/jwks.jsonendpoints
Security Note: For long-term security, we recommend using 3072-bit or 4096-bit RSA keys. The 2048-bit example below is the minimum acceptable key size.
# Generate RSA key pair (3072-bit recommended for long-term security)
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out private.pem -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:3072
openssl rsa -in private.pem -pubout -out public.pem
# For legacy compatibility only (minimum acceptable):
# openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out private.pem -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:2048
# Extract values for JWKS publishing:
# Extract modulus (n) - base64url encoded (single line output)
openssl rsa -in public.pem -pubin -modulus -noout | \
cut -d'=' -f2 | xxd -r -p | base64 | tr -d '=\n' | tr '/+' '_-'
# Generate key ID (kid) - SHA-256 hash of public key
openssl rsa -in public.pem -pubin -outform DER 2>/dev/null | \
openssl dgst -sha256 -binary | base64 | tr -d '=' | tr '/+' '_-'Publish your public keys at https://your-domain.com/.well-known/jwks.json:
{
"keys": [
{
"kty": "RSA",
"n": "<output from n extraction>",
"e": "AQAB",
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "<output from kid generation>"
}
]
}Typically AI agent:
- Makes requests on behalf of users
- Signs JWTs to prove identity
- Encrypts sensitive user data for specific recipients
- Publishes public signing keys via JWKS
Typically Merchant and/or Merchant Vendor:
- Receives authenticated requests
- Verifies JWT signatures from senders
- Decrypts user data encrypted for them
- Publishes public encryption keys via JWKS
| Without the protocol | With the protocol | |
|---|---|---|
| Agent Developers | Your legitimate agent is blocked by aggressive merchant filters or fraudulent usage by other users, leading to failed tasks and frustrated users | Your agent is recognized and trusted by merchant sites, leading to near-100% success rates for login and checkout and higher user satisfaction |
| Merchants | You block all bot traffic to protect your site because you’re unsure what is good or bad, losing out on potential sales and the potential of agentic commerce | You can distinguish between trusted agents and bot threats, enabling you to process more sales and offer personalized experiences based on verified user data |
| Merchant vendors | You struggle to evaluate agent-driven transactions because you can’t distinguish legitimate agents from malicious bots, leading to missed revenue opportunities and strained merchant relationships | You receive verifiable identity and intent data from recognized agents, enabling precise risk assessments, fewer false declines, and stronger merchant trust in your services |
| End-users | Your personal assistant fails to book a flight because it can’t complete a login, gets hit with a CAPTCHA or is blocked as "suspicious" | Your agent acts as a true extension of yourself, recognized and accepted by merchants, with your data and preferences respected |
- Key Size: Use 3072-bit RSA keys (or 4096-bit for highest security)
- Storage: Store private keys securely using hardware security modules (HSM), key management services (AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, HashiCorp Vault), or encrypted at rest
- Version Control: Never commit private keys to version control
- Access Control: Limit access to private keys to essential personnel and services only
Regular key rotation limits the impact of potential key compromise:
- Rotation Schedule: Rotate keys at least annually, or more frequently for high-security applications
- Grace Period: When rotating keys:
- Add the new public key to your JWKS with a new
kid - Keep both old and new keys in JWKS for a transition period (e.g., 24-48 hours)
- Switch to signing with the new private key
- Remove the old public key from JWKS after the transition period
- Add the new public key to your JWKS with a new
- Key Expiration: Consider using the
expfield in JWK to indicate when keys should no longer be used
If a private key is compromised:
- Immediate Action: Remove the compromised public key from your JWKS immediately
- Generate New Key: Create a new key pair and publish the new public key
- Notify Partners: Inform affected recipients of the compromise window
- Audit: Review logs to identify any messages signed during the compromise window
- Short TTL: Use short JWT TTL values (default 1 hour) to limit the window of potential misuse
- Always use HTTPS in production for JWKS endpoints
- Verify SSL certificates
- Use TLS 1.2 or higher
- Expiration: Always check JWT
expclaim; reject expired tokens - Issuer: Verify
issclaim matches expected sender domain - Audience: Verify
audclaim matches your domain - Algorithm: Validate the signing algorithm matches expected values
Recipients MUST implement replay attack prevention by tracking JWT IDs (jti claims):
// Example: Track processed jti values
const processedJtis = new Map(); // or use Redis, database, etc.
async function processMessage(tacMessage) {
const result = await recipient.processTACMessage(tacMessage);
if (result.valid && result.jti) {
// Check if we've seen this jti before
if (processedJtis.has(result.jti)) {
throw new Error('Replay attack detected: duplicate jti');
}
// Store jti with expiration time
processedJtis.set(result.jti, {
processed: Date.now(),
expires: result.expires
});
// Clean up expired entries periodically
cleanupExpiredJtis();
}
return result;
}Implementation Requirements:
- Store
jtivalues for at least the JWT TTL duration (default 1 hour) - Use persistent storage (Redis, database) for production deployments
- Implement periodic cleanup of expired
jtientries - Consider using a bloom filter for high-throughput scenarios
- Ensure all systems use NTP for time synchronization
- The default clock tolerance is 5 minutes (
clockTolerance: 300) - For high-security scenarios, consider reducing tolerance and ensuring tight clock sync
MIT License