Learn how to use struts2 framework.
- Introduction
The Struts framework resides in the web-tier. Struts applications are hosted by a web container and can make use of services provided by the container, such as handling requests via HTTP and HTTPS protocols. This frees developers to focus on building applications that solve business problems.
- Version
2.3.24
-
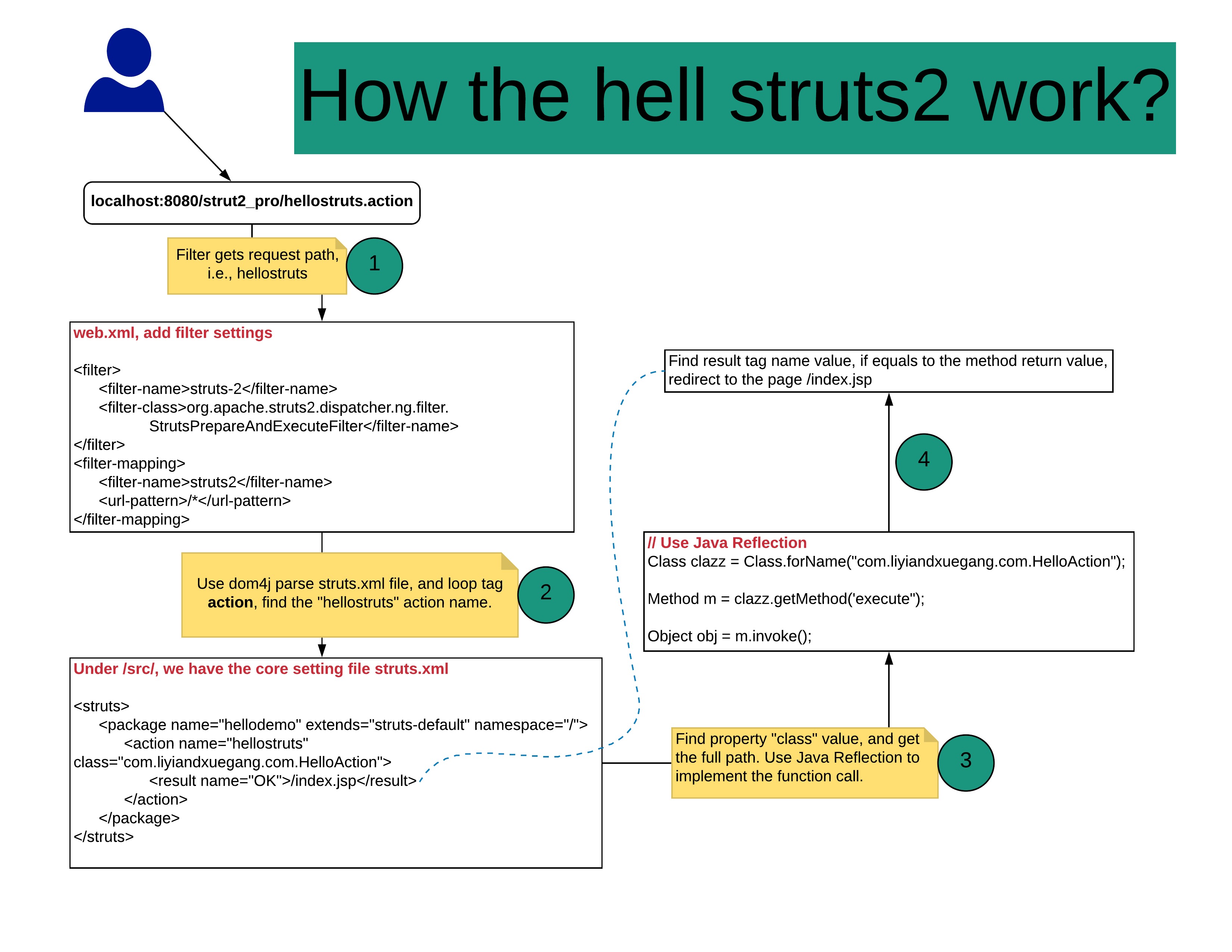
Import jars: Copying from the struts2-blank.war project in the folder apps of struts2-release.
-
Configuration:
** Core file location is fixed, and name it 'struts.xml' **
- Include dtd declarations
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">- Write struts configuration
<struts>
<package name="hellodemo" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<!-- name: The url name -->
<action name="hellostruts" class="com.liyiandxuegang.action.HelloAction">
<result name="ok">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>- Write Filter-mapping (05)
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>- Create HelloAction.java
package com.liyiandxuegang.action;
public class HelloAction {
/*
* [Servlet] 1. Visit servlet, the service() method will be executed.
*
* [Struts2] 2. Similarly, there is a method called execute().
*
*/
public String execute() {
System.out.println("Run through here");
return "ok";
}
}Filter will be created while the server starts, and init() method will be called.
Loading configuration files, including strut2-default.xm, struts2-plugin.xml, and struts.xml
-
Name and location are fixed.
-
Mainly used tags: package, action, and result
-
package: Similar to java code package. All the action should be started as package tag.
-
Properties: 1. name: 2. extends="struts-default", extends action. 3. namespace: by default "/", plus the action name get the access value. /hellostruts
-
Get access route
-
Properties:
-
name: namespace+name value = path name should be unique.
-
class: full path to the class
-
method: by default, action has method "execute".
-
result tag: According to the return-value, send to different path. name same as the method return value. Type: How to send to the path, including forward or include.
struts.i18n.encoding=UTF-8
Write your own configuration file, and include the xml file in the main file.
<!--If you have struts-hello.xml-->
<struts>
<include file="com/liyiandxuegang/action/struts-hello.xml"></include>
</struts>- Use tag action method property. If Action methods have return-value and type must be String. If return value void, return none;
<!--If action has few methods-->
<action name="addbook" class="com.liyiandxuegang.methods.BookAction" method="addBook" />
<action name="updatebook" class="com.liyiandxuegang.methods.BookAction" method="updateBook" />- General *
** method = {1} **
<!--If we thousands of methods? -->
<struts>
<package name="methoddemo" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="func_*" class="com.liyiandxuegang.methods.GeneralFuncsAction" method="{1}" />
</package>
</struts>// GeneralFuncsAction.java
public class GeneralFuncsAction extends ActionSupport{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String add(){
System.out.println("add function");
return NONE;
}
public String update() {
System.out.println("update function");
return NONE;
}
}- Use global result page
If we have two functions, which returns the same value. We can use global-results
<struts>
<package name="global_method" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<global-results>
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<action name="book" class="com.liyiandxuegang.action2.BookAction" />
<action name="order" class="com.liyiandxuegang.action2.OrderAction" />
</package>
</struts>- Local result page
<struts>
<package name="global_method" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="book" class="com.liyiandxuegang.action2.BookAction">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>- 如果同时配置了两个页面,局部页面有效。
- For redirecting to pages, there are two values. dispatcher or redirect.
<result name="success" type="redirect">/index.jsp</result>- If to other actions, there are two values: chain or redirectAction.
Ex: /book ---> page /order
<action name="book" class="com.liyiandxuegang.action2.BookAction">
<result name="success" type="redirectAction">order</result>
</action>web阶段,servlet使用request对象获取对象。
How to get request object?
- Use ActionContext
We have a form page:
<h1>Hello, Struts</h1>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/form1.action" method="post">
User name: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="pwd"><br>
Address: <textarea rows="30" cols="50" name="address"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>And we have the seting file, called, struts-form.xml.
<struts>
<package name="formSubmit" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="form1" class="com.liyiandxuegang.form.Form1Action">
<result name="none">/success.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>In our java file, we do accept the parameter value.
public class Form1Action extends ActionSupport{
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
// Use method 1, ActionContext
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
Map<String, Object> map = actionContext.getParameters();
// loop map
Set<String> keysSet = map.keySet();
for(String key : keysSet) {
// Value is in array format.
Object[] obj = (Object[]) map.get(key);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obj));
}
return NONE;
}
}- User ServletActionContext
Similarly, we create one function.
public String testServletActionContext() {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
String username= httpServletRequest.getParameter("username");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("pwd");
String address = httpServletRequest.getParameter("address");
System.out.println(username + ", " + password + ", " + address);
return NONE;
}This is static function, so it is much easier to get the request value.
- Use interface injection
- how to use request, session, servletContext object in Action.
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
httpServletRequest.setAttribute("username", username);
HttpSession session = httpServletRequest.getSession();
session.setAttribute("sess", "sessVal");ServletContext doesn't use much.
- Struts2 封装获取数据的方法
- Use original way
Imagine we have an Entity named "User"
package com.liyiandxuegang.entity;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private String address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.getUsername() + ", " + this.getPassword() + ", " + this.getAddress();
}
}And Action Class named Form2Action
public class Form2Action extends ActionSupport{
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
String username = httpServletRequest.getParameter("username");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("pwd");
String address = httpServletRequest.getParameter("address");
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
user.setAddress(address);
System.out.println(user);
return NONE;
}
}** After we submit the form, we can get and set the Entity value in the action.**
Struts2提供的封装方式:
- 属性封装
在action成员变量位置定义变量,变量名称和表单输入项的name属性值一样。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/data" method="post">
User name: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="pwd"><br>
Address: <textarea rows="30" cols="50" name="address"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>In action class,
public class Date1Action extends ActionSupport{
private String username;
private String pwd;
private String address;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(username + ", " + pwd + ", " + address);
return NONE;
}
}After you click submit the form, the data has been binded to the Action Support member fields.
- 模型驱动封装: 可以把数据直接封装到实体对象里面
-
Keep the form fields name the same as the Entity properties name.
-
Easy to implement in Action class
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/data1" method="post">
User name: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
Address: <textarea rows="30" cols="50" name="address"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>- Create the Entity class and implement the function getModel();
public class Data2Action extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User>{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private User user = new User();
@Override
public User getModel() {
return user;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(user);
return NONE;
}
}- 使用模型驱动和属性封装需要注意的问题:
在一个action中,获取表单数据可以属性封装,也可以使用模型驱动封装,不能同时使用属性封装和模型驱动封装。
- 表达式封装
-
在action里面声明实体类
-
生成实体类变量的set和get 方法
-
在表单输入项的name属性值里面写表达式形式
public class Data3Action extends ActionSupport{
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println(user);
return NONE;
}
}and in jsp file
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/data3" method="post">
User name: <input type="text" name="user.username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="user.password"><br>
Address: <textarea rows="30" cols="50" name="user.address"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>比较表达式封装和模型驱动封装:
-
两者都可以把数据封装到实体类中。
-
在模型驱动中只能将数据封装到一个实体类中。使用表达式封装就可以把数据封装到不同的实体类中。[15]
Similar to EL expression. OGNL不是Struts2的一部分。
在struts2把数据放到值栈中,在页面中获取值栈数据。
Servlet和action区别:
Servlet对象默认第一次访问是创建,创建一次,单实例对象。
Action访问时创建,每次访问时都会创建一个action对象。
值栈的存储位置:每个action对象 只有一个值栈对象。
Use ActionContext get value stack.
// get ActionContext obj
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
// get valuestack obj
ValueStack valueStack = context.getValueStack();值栈中两部分内容:
-
root 就是 List集合
-
context 是Map集合
常用的就是root集合。[06]