An advanced AI-powered platform for atomistic microscopy simulations, combining multi-agent workflows, machine learning potentials, and LLM-assisted analysis to simulate surface structures across multiple experimental techniques.
Watch how µStack works in action:
Click the image or click here to watch the full demo on YouTube to see µStack simulating atomistic microscopy workflows.
- STM (Scanning Tunneling Microscopy): DFT-based simulations using GPAW with LDOS calculations
- IETS (Inelastic Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy): Spectroscopic analysis via pyPPSTM integration
- TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy): Multislice wave-function simulations with abTEM
- AFM (Atomic Force Microscopy): Tip-sample interaction modeling with ppafm OpenCL acceleration
- LangGraph-based multi-agent system: Sequential routing of structure generation → relaxation → microscopy simulations
- Session-aware execution: Reuse structures across multiple microscopy techniques without regeneration
- Intelligent command chaining: Execute relaxation→STM→IETS in a single workflow
- Real-time progress tracking: WebSocket-enabled status updates for long-running simulations
- Multi-backend support: SciLink LLM-powered generation with Materials Project database fallback
- FCC metal surfaces: Cu, Pt, Au, Ag, Ni, Pd on (100), (111), and (110) faces
- 2D materials: Graphene and MoS₂ with automatic lattice parameter optimization
- Session persistence: Generated structures available for subsequent simulations without regeneration
- MACE-MP potential: Universal machine learning potential trained on ~150k Materials Project DFT calculations
- FIRE optimization: Fast inertial relaxation with GPU acceleration support
- Physical validation: Automatic vacuum correction and structure validation
- Multi-LLM support: Claude (Anthropic), DeepSeek, and Google Gemini for query parsing and report generation
- Intelligent query parsing: Natural language understanding of simulation requests
- Automated reports: AI-generated discussion sections with physics interpretation and literature comparisons
- NSID metadata: Scientific data export via NSID format for standardized experimental data representation
- Interactive CLI: Rich terminal UI with markdown rendering and real-time progress updates
- FastAPI Web API: Modern REST API with WebSocket support for async simulation execution
- Session management: Global session tracking across CLI and web interfaces
- File serving: Automatic static file serving of generated images and data files
pip install microstackThis installs the microstack package and registers the CLI command.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/blaiszik/microstack.git cd microstack -
Install in editable mode:
pip install -e .
- Python: 3.12 or higher
- Memory: 16+ GB recommended for large structure simulations
- GPU (recommended): CUDA-capable GPU for accelerated relaxation and STM calculations
- GPAW and MACE models benefit significantly from GPU acceleration
- CPU-only operation is supported but slower
Set up environment variables for API access:
# For Anthropic Claude (AI report generation)
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-ant-..."
# For Materials Project database queries (optional)
export MP_API_KEY="your-mp-api-key"
# For Google Gemini (alternative LLM)
export GOOGLE_API_KEY="your-google-api-key"
# For DeepSeek (alternative LLM)
export DEEPSEEK_API_KEY="your-deepseek-api-key"Or create a .env file in your working directory with the above variables.
microstack --help
microstack check-configStart the interactive CLI:
microstackThis launches an interactive chat interface where you can describe what you want to simulate in natural language.
Terminal Features:
- Rich markdown rendering with syntax highlighting
- Real-time progress tracking and status updates
- Interactive multi-step workflow support
- Formatted reports with embedded metrics and visualizations
Use natural language to request simulations:
microstack> relax Cu 100
microstack> analyze Pt 111 with STM
microstack> generate graphene and run STM and IETS
microstack> run TEM on gold 111
microstack> relax and scan with AFM
microstack> help
microstack> quit
Launch the FastAPI web server:
microstack web --port 8000Access the UI at http://localhost:8000 to submit queries via a modern web interface with real-time progress tracking.
Web Interface Features:
- Modern responsive design with real-time updates
- Query submission and progress monitoring
- Gallery view of generated images and results
- Session management and result history
- Direct access to simulation data and reports
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
microstack |
Enter interactive mode |
microstack interactive |
Explicitly start interactive chat |
microstack web |
Start FastAPI web server |
microstack check-config |
Validate API keys and GPU availability |
microstack --help |
Show all available commands |
Single Microscopy Technique:
microstack interactive
# Type: relax Cu 100 and run STMMulti-Technique Chain:
# Relax structure, then run STM followed by IETS (all in one workflow)
microstack> relax Pt 111 and scan with STM then IETSCustom Parameters:
# Natural language parameter control
microstack> relax Au 111 with 300 relaxation steps and simulate with STM at 5 angstrom heightSession Reuse:
# Generate structure once, analyze with multiple techniques
microstack> generate Cu 100 surface
microstack> run STM on current structure
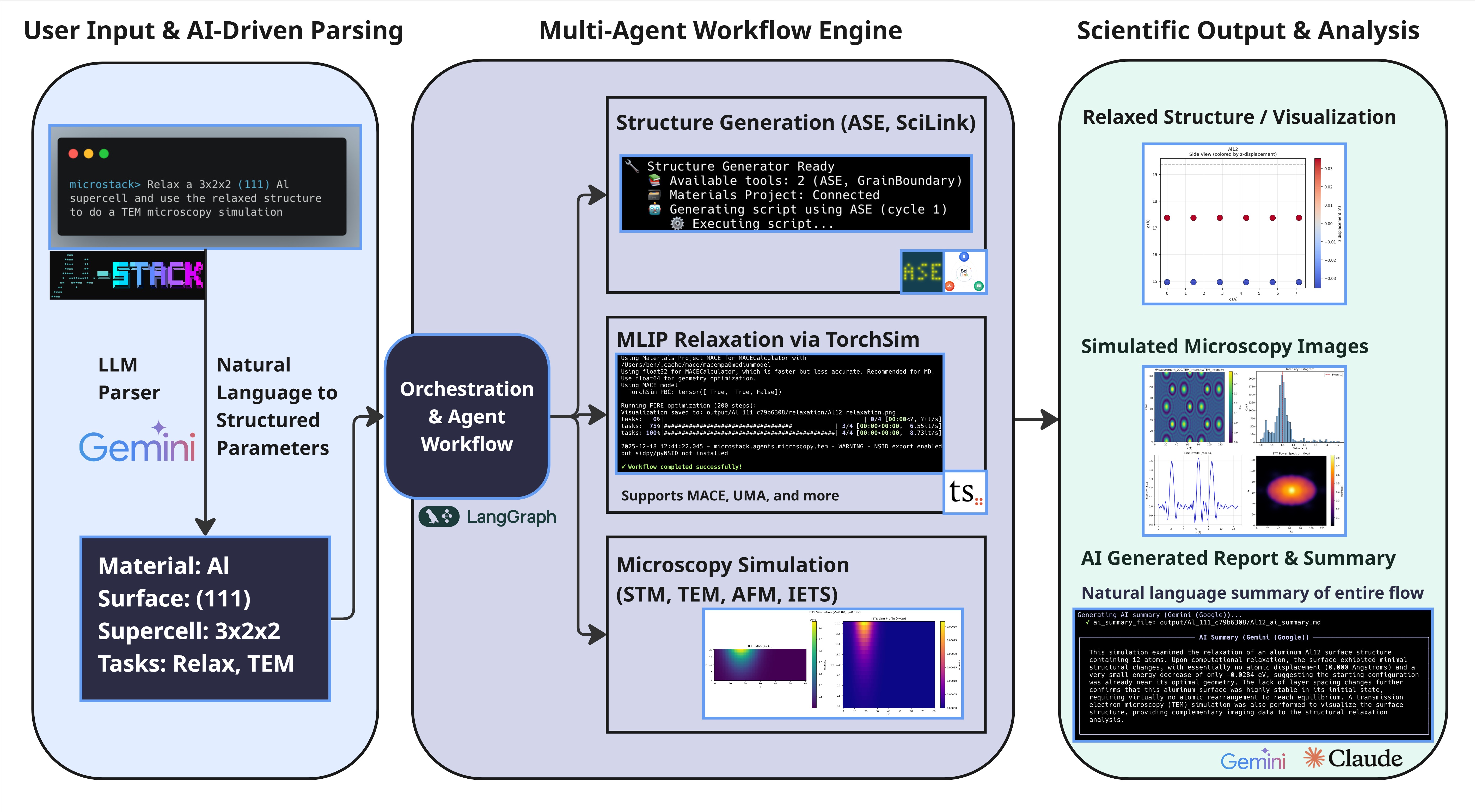
microstack> run AFM on current structureµStack uses a state-machine-based workflow orchestrated by LangGraph, enabling sophisticated multi-step simulations:
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ µ-STACK WORKFLOW PIPELINE │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
User Query
↓
[1] QUERY PARSING (LLM)
├── Input: "relax Pt 111 and run STM then IETS"
├── LLM Agent: Parse with Claude/DeepSeek/Gemini
└── Output: task_type, material, face, microscopy_queue=[STM, IETS]
↓
[2] STRUCTURE GENERATION
├── Backend Selection:
│ ├── SciLink (LLM-powered structure generation)
│ └── Materials Project Database (DFT reference + ASE builder)
├── Session Awareness: Reuse existing structure if already generated
└── Output: atoms_object (ASE Atoms) + structure metadata
↓
[3] STRUCTURE RELAXATION (Optional)
├── Potential: MACE-MP universal ML potential (~150k DFT data)
├── Optimizer: FIRE (Fast Inertial Relaxation Engine)
├── GPU Support: CUDA-accelerated force calculations
└── Output: relaxed_structure + energy_change + displacement metrics
↓
[4] MICROSCOPY ROUTING
├── Queue Processing: Execute microscopy techniques in order
├── Session Persistence: Reuse relaxed structure for all techniques
└── Parallel Capability: Independent simulations chain seamlessly
↓
[5] TECHNIQUE-SPECIFIC SIMULATION
│
├── STM (Scanning Tunneling Microscopy)
│ ├── Engine: GPAW DFT calculator
│ ├── Output: LDOS (Local Density of States) maps
│ ├── Visualization: Energy-resolved topography images
│ └── File: stm_topography_<height>.png + stm_ldos.npy
│
├── IETS (Inelastic Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy)
│ ├── Engine: pyPPSTM (PPSTM fork)
│ ├── Output: Spectroscopic d²I/dV² curves
│ ├── Visualization: Energy-dependent conductance maps
│ └── File: iets_spectrum.png + iets_data.npy
│
├── TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy)
│ ├── Engine: abTEM multislice wave-function propagation
│ ├── Output: Phase shift and intensity maps
│ ├── Visualization: Diffraction patterns + BF/DF images
│ └── File: tem_bright_field.png + tem_diffraction.png
│
└── AFM (Atomic Force Microscopy)
├── Engine: ppafm with OpenCL GPU acceleration
├── Output: Tip-sample force maps (conservative + dissipative)
├── Visualization: Height maps and 3D surface topography
└── File: afm_height.png + afm_forces.npy
↓
[6] AI-ASSISTED ANALYSIS
├── Physics Interpretation: Claude analyzes results
├── Literature Comparison: Cross-reference with experimental data
├── Report Generation: Markdown with embedded images and data
└── File: simulation_report.md + results_summary.txt
↓
[7] DATA EXPORT
├── NSID Format: Standard scientific data structure
├── Output Directory: Session-organized hierarchical structure
└── Files: All images, raw data (NPY), metadata (JSON), reports (MD)
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
agents/workflow.py |
LangGraph state machine orchestrating multi-agent pipeline |
agents/state.py |
WorkflowState Pydantic model tracking execution lifecycle |
agents/session_manager.py |
Global session tracking and state persistence |
agents/structure_generator.py |
Multi-backend structure generation with session reuse |
agents/microscopy_router.py |
Queue-based routing for sequential microscopy execution |
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
agents/microscopy/stm.py |
STM simulations with GPAW DFT + LDOS calculations |
agents/microscopy/iets.py |
IETS spectroscopy via pyPPSTM integration |
agents/microscopy/tem.py |
TEM simulations using abTEM multislice propagation |
agents/microscopy/afm.py |
AFM tip-sample interactions with ppafm OpenCL |
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
llm/client.py |
Unified LLM factory supporting Anthropic, DeepSeek, Gemini |
llm/models.py |
Pydantic schemas for query parsing and response validation |
llm/prompts.py |
Structured prompts for LLM agents |
llm/anthropic.py |
Anthropic Claude integration |
llm/deepseek.py |
DeepSeek API client |
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
relaxation/generate_surfaces.py |
ASE-based surface structure generation |
relaxation/surface_relaxation.py |
MACE potential + FIRE optimizer |
relaxation/materials_project.py |
Materials Project API queries + LEED reference data |
relaxation/relax_report_generator.py |
Relaxation analysis and AI report generation |
relaxation/scilink_integration.py |
SciLink structure generation backend |
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
cli/app.py |
Click CLI with main commands |
cli/interactive.py |
Interactive chat mode with rich formatting |
web/api.py |
FastAPI REST API with WebSocket support |
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
utils/config.py |
API keys, paths, and environment management |
utils/settings.py |
Pydantic settings for all microscopy parameters |
utils/gpu_detection.py |
GPU capability detection and CUDA validation |
utils/logging.py |
Rich-based logging with color output |
io/nsid.py |
NSID scientific data export format |
STM provides sub-angstrom resolution imaging by measuring tunneling current between a sharp tip and sample. µStack uses GPAW (DFT calculator) to compute local density of states (LDOS).
Key Parameters:
- Tip height (z): 2-10 Å above surface
- Bias voltage (V): -2 to +2 V for spectroscopy
- Temperature: Affects thermal smearing of LDOS
Outputs:
- Constant-height topography images
- Energy-resolved LDOS maps
- Scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS) curves
IETS detects inelastic scattering of tunneling electrons, revealing vibrational modes and electronic excitations. µStack integrates pyPPSTM (modified PPSTM).
Key Parameters:
- Modulation frequency: Lock-in detection of conductance changes
- Energy resolution: ~1-10 meV
- Spatial resolution: ~0.1-0.5 nm (poorer than STM)
Outputs:
- d²I/dV² spectroscopic maps
- Vibrational mode identification
- Electronic excitation energies
TEM transmits electrons through thin structures, providing atomic-resolution crystallographic information. µStack uses abTEM multislice simulations.
Key Parameters:
- Accelerating voltage: Typically 100-300 keV
- Slice thickness: ~1-2 Å for convergent-beam analysis
- Scattering angle: Low-angle (bright field) to high-angle (dark field)
Outputs:
- Phase shift maps
- Bright-field/dark-field images
- Convergent-beam electron diffraction (CBED) patterns
- Effective specimen thickness variations
AFM measures tip-sample forces by monitoring cantilever deflection, enabling force mapping and nanomechanical characterization. µStack integrates ppafm with OpenCL GPU acceleration.
Key Parameters:
- Probe particle: Effective probe radius (typically 1-5 Å)
- Scan height: 2-5 Å above surface
- Force components: Conservative (elastic) + dissipative (energy loss)
Outputs:
- 3D height maps
- Conservative force maps
- Dissipative force maps (energy landscapes)
- 3D surface topography
All results are organized hierarchically by session:
output/
├── session_<id>/ # Session directory
│ ├── structure/
│ │ ├── structure_unrelaxed.xyz
│ │ ├── structure_relaxed.xyz
│ │ └── structure_info.json
│ │
│ ├── stm/ # STM results (if requested)
│ │ ├── stm_topography.png
│ │ ├── stm_ldos_map.npy
│ │ └── stm_config.json
│ │
│ ├── iets/ # IETS results (if requested)
│ │ ├── iets_spectrum.png
│ │ ├── iets_data.npy
│ │ └── iets_config.json
│ │
│ ├── tem/ # TEM results (if requested)
│ │ ├── tem_bright_field.png
│ │ ├── tem_diffraction.png
│ │ ├── tem_phase_shift.npy
│ │ └── tem_config.json
│ │
│ ├── afm/ # AFM results (if requested)
│ │ ├── afm_height.png
│ │ ├── afm_conservative_force.npy
│ │ ├── afm_dissipative_force.npy
│ │ └── afm_config.json
│ │
│ ├── analysis/
│ │ ├── workflow_report.md
│ │ ├── relaxation_metrics.json
│ │ └── comparison_data.json
│ │
│ └── nsid/ # NSID format export
│ └── data.h5 # HDF5 with standardized scientific metadata
microstack/
├── pyproject.toml # PyPI packaging configuration
├── README.md # This documentation
├── LICENSE # MIT License
├── assets/ # Images for documentation
│ ├── microstack-logo.png
│ ├── microstack-workflow.jpg
│ └── microstack-terminal.png
│
└── src/microstack/ # Main package
├── __init__.py
│
├── cli/ # Command-line interface
│ ├── app.py # Main CLI entry point
│ └── interactive.py # Interactive mode
│
├── agents/ # LangGraph agents
│ ├── workflow.py # State machine orchestration
│ ├── state.py # WorkflowState schema
│ ├── session_manager.py # Session lifecycle management
│ ├── structure_generator.py # Structure generation
│ ├── microscopy_router.py # Microscopy execution router
│ └── microscopy/ # Technique-specific agents
│ ├── stm.py
│ ├── iets.py
│ ├── tem.py
│ └── afm.py
│
├── llm/ # Language model integration
│ ├── client.py # LLM factory
│ ├── anthropic.py
│ ├── deepseek.py
│ ├── models.py # Pydantic schemas
│ └── prompts.py
│
├── relaxation/ # ML structure relaxation
│ ├── generate_surfaces.py
│ ├── surface_relaxation.py
│ ├── materials_project.py
│ ├── relax_report_generator.py
│ └── scilink_integration.py
│
├── web/ # FastAPI web interface
│ ├── api.py # REST API + WebSocket
│ └── __init__.py
│
├── io/ # Data I/O
│ ├── nsid.py # NSID format support
│ └── __init__.py
│
├── utils/ # Utilities
│ ├── config.py # Configuration management
│ ├── settings.py # Pydantic settings
│ ├── gpu_detection.py
│ ├── logging.py
│ ├── report_generator.py
│ └── exceptions.py
│
└── output/ # Generated results (at runtime)
µStack integrates multiple mature scientific computing libraries:
- GPAW (DFT calculator): STM and relaxation simulations via density functional theory
- pyPPSTM: Inelastic electron tunneling spectroscopy calculations
- abTEM: Transmission electron microscopy multislice wave-function propagation
- ppafm: Atomic force microscopy tip-sample interaction modeling with OpenCL
- MACE-MP: Universal ML potential trained on ~150k Materials Project DFT calculations
- torch: PyTorch backend for MACE force calculations and GPU acceleration
- ASE (Atomic Simulation Environment): Structure generation and manipulation
- SciLink: AI-powered structure generation via Claude API
- Materials Project API: Access to 150k+ computed material properties
- LangGraph: Multi-agent state machine orchestration
- FastAPI: Modern REST API with async support
- Uvicorn: ASGI web server with WebSocket support
- Click: Command-line interface framework
- Rich: Terminal UI with markdown rendering
- NumPy/Matplotlib: Numerical computing and visualization
- Pydantic: Data validation and settings management
- pyNSID/sidpy: Scientific data standardization (NSID format)
- h5py: HDF5 file handling
- Anthropic: Claude API for query parsing and report generation
- DeepSeek: Alternative LLM provider
- Google Generative AI: Gemini model support
µStack welcomes contributions! Areas for improvement:
- New microscopy techniques: Add support for XRD, HREELS, LEED, etc.
- Additional ML potentials: Integrate other universal potentials (MACE variants, CHGNet, etc.)
- Performance optimization: CUDA kernels for common bottlenecks
- Documentation: Tutorials, physics background, troubleshooting
- Testing: Comprehensive unit and integration tests
- UI improvements: Enhanced web interface and visualization
If you use µStack in published research, please cite:
@software{microstack2025,
title={µStack: Multi-Agent Atomistic Microscopy Simulation Platform},
author={Team µStack},
year={2025},
url={https://github.com/blaiszik/microstack},
version={0.1.0}
}µStack Core Team:
- Aritra Roy (contact@aritraroy.live)
- Kevin Shen (kevin.shen@noble.ai)
- Ben Blaiszik (blaiszik@uchicago.edu)
- Piyush Ranjan Maharana (piyushmaharana15@gmail.com)
µStack builds on the work of multiple open-source projects:
MIT License - see LICENSE file for details
Copyright (c) 2025 Team µStack
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
Made with ❤️ by the µStack Team
Built for the materials science and microscopy research community during the 2025 Microscopy Hackathon.
For questions, feedback, or collaborations: GitHub Issues