With this repository, we show that it is possible to separate groups of attacked text samples from each other. We do this using a Siamese neural network that is trained to embed representations of textual adversarial examples.
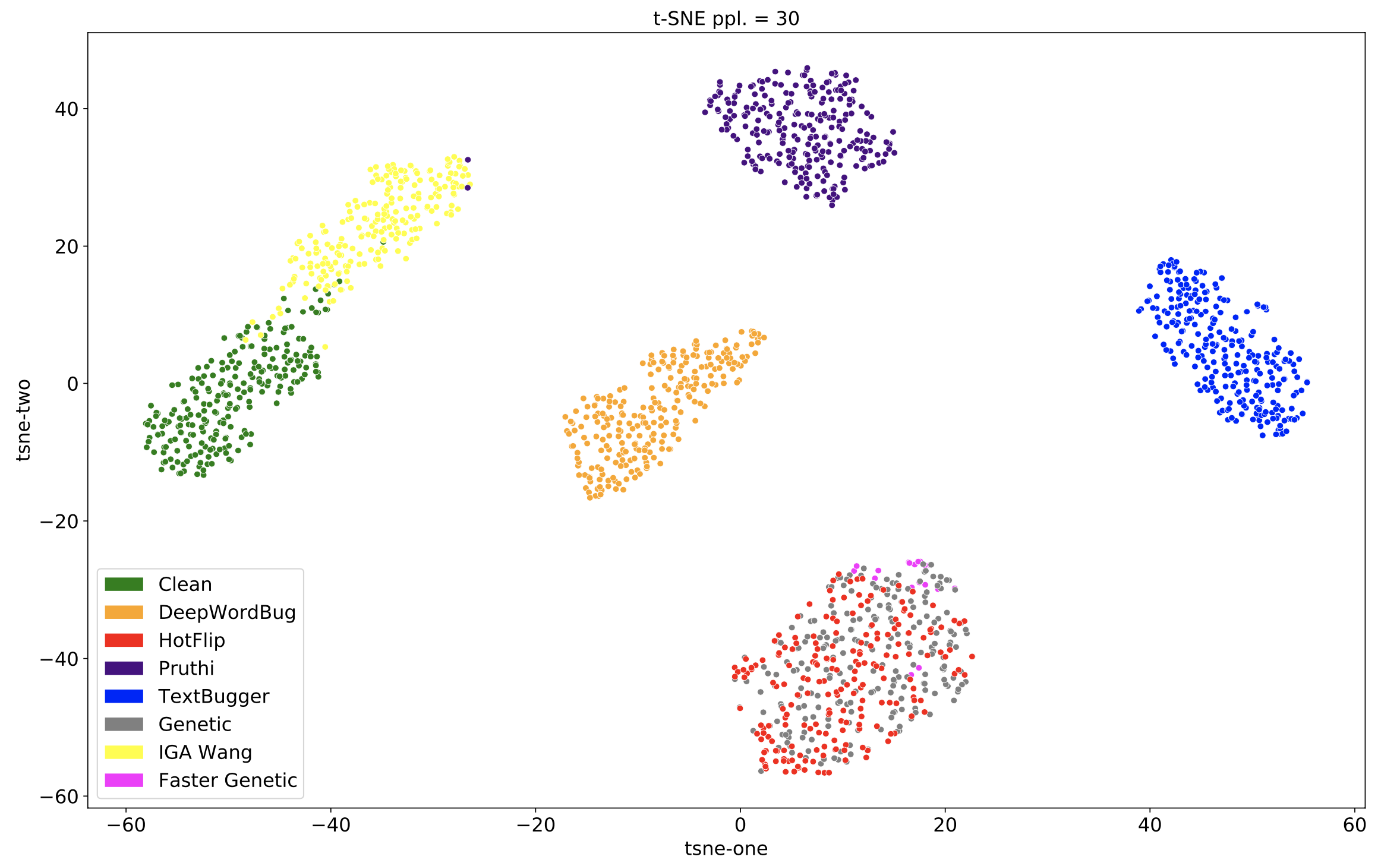
In the image from the demo below, you can see that different attackers (Pruthi, HotFlip, Genetic, etc.) tend to produce adversarial examples that appear in different locations of the embedding space when visualized using t-SNE.
Check out the demo to see how different groups of attacks get embedded by the trained Siamese network!
Things to note about the demo:
- The attacks shown are successful SST-2 attacks created for all three target models (BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNET).
- Each point on the t-SNE plot represents the average of a group of embeddings for 15 attacked samples.
- The Siamese network was trained on DeepWordBug, HotFlip, Pruthi, TextBugger, and the "Clean" attack (the Clean attack does nothing and leaves the original text sample unchanged). The Siamese network did not see Faster Genetic, Genetic, or IGA Wang samples during training.
- In the t-SNE plot, the black "X" shows where the currently selected group of attacked samples gets embedded by the Siamese network.
- The table below the t-SNE plot lists the text samples that are in this group of 15.
- You can change which attacker and which group of attacked samples you are inspecting with the drop downs in the left sidebar.
The scripts that do a lot of the heavy lifting are:
train_siamese.pyand the associated SLURM job files injobs/siamese/allow one to train a Siamese network to embed textual attacks (extracted using the REACT feature extraction pipeline)eval_siamese.pyand the associated SLURM job files injobs/evalallow one to evaluate a trained Siamese network on the task of novelty prediction using: (1) distance to the known attack mean embeddings, (2) Local Outlier Factor in the Siamese network embedding space. These also run the same/different novel attack prediction experiments where the task is to determine if two groups were created by the same novel attack method or not.train_clf.pyand the associated SLURM job files injobs/classifyallow one to train a boosted tree classifier for attack labeling and then evaluate the trained classifier on the task of novelty prediction using the output entropy of the classifier
The following two scripts are also somewhat important:
analyze_variants.pyand the associated SLURM job files injobs/variantsallow for one to determine how similar/different variant attacks are to/from their original attack methodscluster.pyand the associated SLURM job files injobs/clusterallow one to cluster attacks using various clustering algorithms such as k-means. This script has not been updated in a while and is close to being deprecated.
Clone this repository and cd into it.
If you do not already have a conda environment with Python 3.8 installed, create a new conda environment with 3.8. Now activate this environment.
In this conda environment, run $ pip install -r requirements.txt in order to install the required packages.
The links below are outdated. Please contact Adam Noack at adamnoack1@gmail.com if you want the data.
To run any of the scripts in this repository, you will need to download the joblib files that hold the extracted features for the attacks. They should be in the shared Google Drive folder. Create this directory structure react-cluster/data/extracted_features/ and then place the downloaded joblib files into the extracted_features/ subdirectory.
To run any of the SLURM job files in jobs/*/, you will have to create the following three directories: react-cluster/jobs/errors/, react-cluster/jobs/logs/, and react-cluster/output/, and as one might expect, the errors, logs, and output directories from the scripts will show up in these directories, respectively.
If running analyze_variants.py you will need to download whole_dataset_with_meta.csv, and if you are running cluster.py you will also need to download whole_catted_dataset.csv from the shared Google Drive folder. Create this directory structure react-cluster/data/original_data/ and then place the downloaded CSV files into the original_data/ subdirectory. You will also have to download the actual text produced by the variants which can be found by navigating down the Google Drive directory structure starting here.