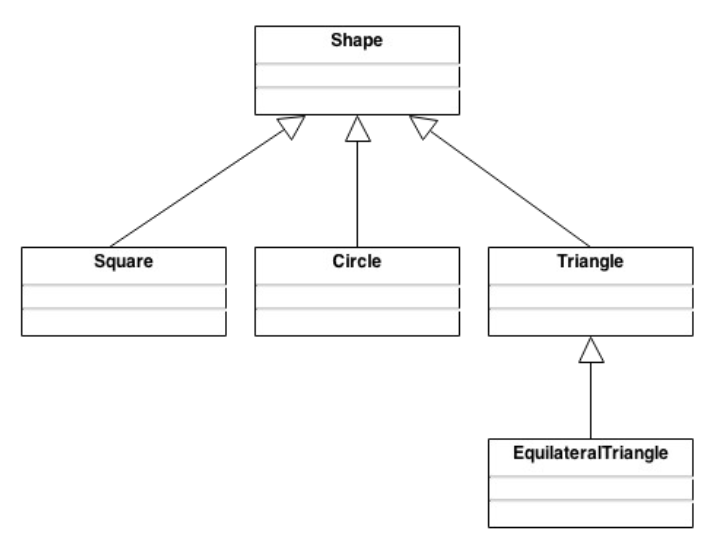
Description: Shapes and Objects using Kotlin. There is a superclass (Shape) and there are 3 subclasses of Shape (Circle, Square, Triangle). Each of these subclasses extends Shape as each of them is a shape, however they differ with each object, and require different methods to calculate the area for each, and there are different values that need to be stored as dimensions. Finally, there is a 4th class (Equilateral Triangle) which extends the triangle class. This is slightly different as all 3 sides are the same, wheras with the normal triangle class, all 3 sides could be different.
An abstract class, the shape class is meant to act as a board for the other classes, as they are all shapes, but all differ slightly, requiring different values and different methods of calculating the area of the object. The methods in the superclass are overwritten, except for the showName() function that is called in each object's PrintDimensions() function that is override.
Takes in the radius from the user, stored as a private double variable. Radius is initialized to 0.0 until the user enters in the value of the radius. setDimensions() is called in main and the value of radius changes, and finally the getArea() function is called using Kotlin's math.pow() function to get exponent and the math.PI value is used to finalize the area calculation. PrintDimensions() funtion is called when the values of all objects are input by the user, and print all values to the screen.
Takes in the length and height of the object from the user, stored as a private double variable. Height and Length are initialized to 0.0 until the user enters in the values of the height and length. setDimensions() is called, taking in the height and length values from the user as Doubles, not Integers, and changing the values of the private variables from 0.0 to what user input. Finally, getArea() function is called to calculate the area of the object, in this case, length * width, and then returned as a double. The PrintDimensions() function is called when the values of all objects are input by the user, and prints all values to the screen
Takes the lengths of the 3 sides of the object from the user, stores each of them as a private double variable. All side lengths are initialized to 0.0 until the
user enters in the values of the height and length. SetDimensions() is called, taking the 3 side lengths from the user as Doubles, and changing the values of the
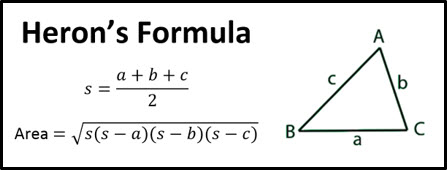
private variables from 0.0 to what the user inputs. Finally, getArea() functio is called to calculate the area of the object, in this case, using Heron's formula
to calculate the value of the area of the object. PrintDimensions() function is called when the values of all objects are input by the user, and prints all values
to the screen.
An extension of the Triangle Object class, only occurs when all three values of the sides are the same length, stored as only 1 private double variable. Initialized to 0.0 until the user inputs a value. SetDimensions() is called, in this case override is used, as set dimensions already exists in the superclass, but in the subclass only 1 side is used not three. Finally, getArea() function is called to calculate the area of the object and returned as a double. PrintDimensions() function is called when all values for all objects are input by the user, and prints all values to the screen.